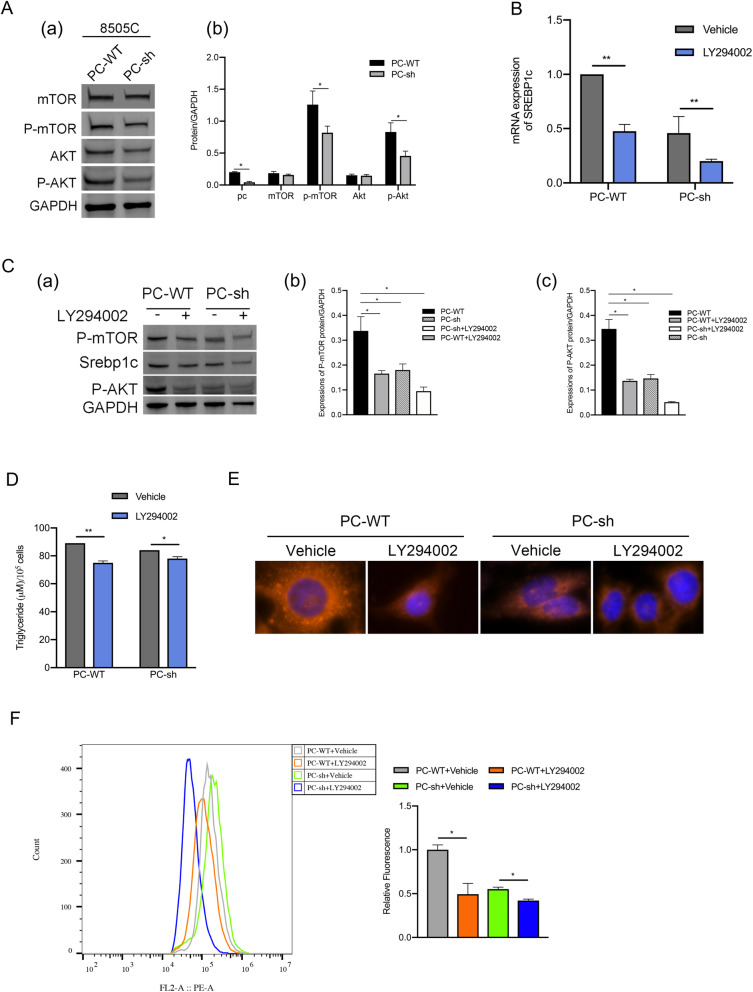
Fig. 5.
PC upregulates the expression of SREBP1c by activating the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. (A) a. Western blot analysis of phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt), mTOR and phosphorylated mTOR (p-mTOR) in 8505C/PC-WT and 8505C/PC-sh cells; the full blot is provided in supplementary file. b. Quantitative analysis of the expression of each protein. * p < 0.05, compared with the PC-WT group. B qRT-PCR analyses of SREBP1c mRNA in different 8505C cells treated with the Akt inhibitor LY294002. (C) a. Western blot analysis of the protein expression of SREBP1c, p-Akt, and p-mTOR in different 8505C cells treated with an Akt inhibitor, LY294002; the full blot is provided in supplementary file. b. Quantitative analysis of p-mTOR protein expression. * p < 0.05, compared with the PC-WT group. c. Quantitative analysis of p-AKT protein expression. * p < 0.05, compared with the PC-WT group. D The cellular TAG content was measured in different 8505C cells. E Nile red dye and DAPI staining were used to detect the neutral lipid content in 8505C cells by microscopy with a 40× objective lens. F 8505C/PC-WT cells treated with LY294002 and 8505C/PC-sh cells treated with LY294002 were stained with Nile red dye and subjected to flow cytometry analysis. The results are expressed as means ± standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments and shown in histograms on the right. * p < 0.05; *** p < 0.01 versus 8505C/PC-WT cells treated with vehicle and 8505C/PC-sh cells treated with vehicle. Note: mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin)