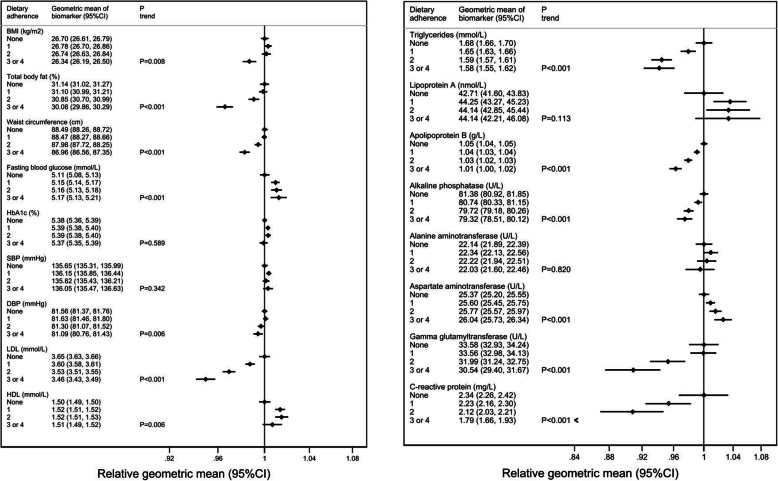
Fig. 2.
Associations between adherence to total dietary recommendations (WHO) and baseline cardiometabolic risk factors (n = 32,728). Abbreviations: BMI (body mass index), HbA1c (glycated haemoglobin), SBP (systolic blood pressure), DBP (diastolic blood pressure), LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, and CI (confidence intervals). Adjusted means, 95%CI, and p-trends were estimated through multivariable logistic regression. Models included age, sex, ethnicity (Whites, others, unknown), region (England, Scotland, Wales), Townsend index of deprivation (quintiles 1–5 or unknown, with lower scores representing greater affluence), education group (vocational qualifications [NVQ, HND, HNC], any school degree [A-level, AS-level, O-level, GCSE, CSE], higher degree [college, university, of professional degree/qualification], none of the above, unknown), smoking status (never, previous, current, unknown), physical activity (continuous, total MET-hours/week), alcohol consumption (none, occasional < 1 unit/week, moderate 1–14 units/week, heavy > 14 units/week, unknown), menopausal status (yes, no, not applicable [men]), and log-transformed total daily energy as covariates