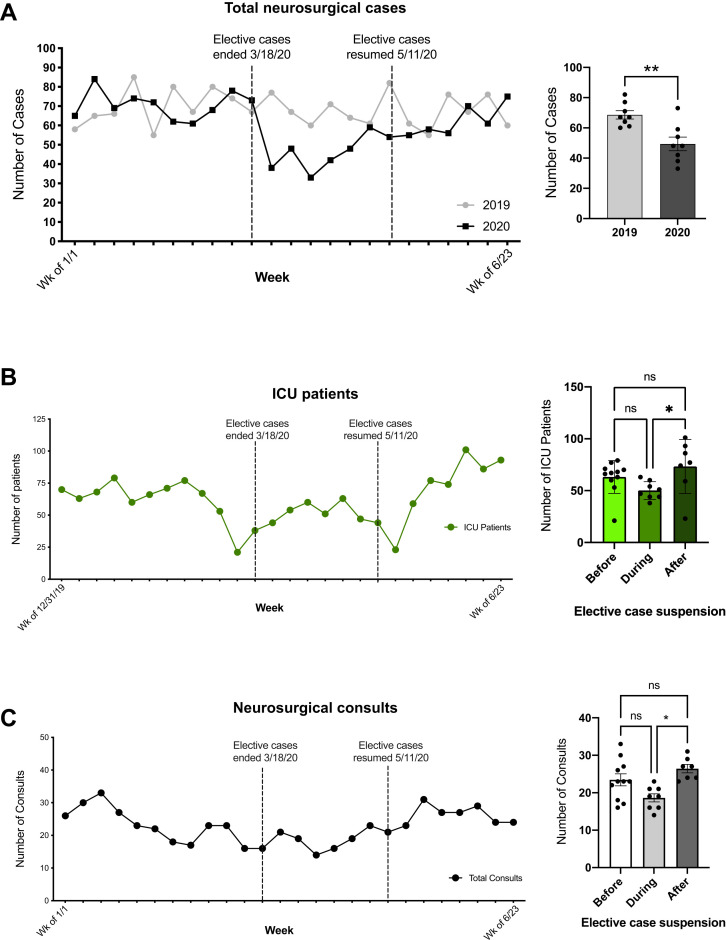
Figure 1.
Neurosurgery cases decreased after elective cases were suspended. (A) Total number of neurosurgical cases shown from January 1 to June 23 of 2019 and 2020. During elective case suspension, neurosurgical cases dropped to 48% of baseline cases. The number of cases during the window of suspension was significantly lower in 2020 compared with the same timeframe in 2019 (P = 0.0025). (B) There were significantly fewer (non-COVID-19) intensive care unit patients during the window of suspension compared with after the suspension (P = 0.045). (C) There were significantly fewer neurosurgical consults during the window of suspension compared with after the suspension (P = 0.04).