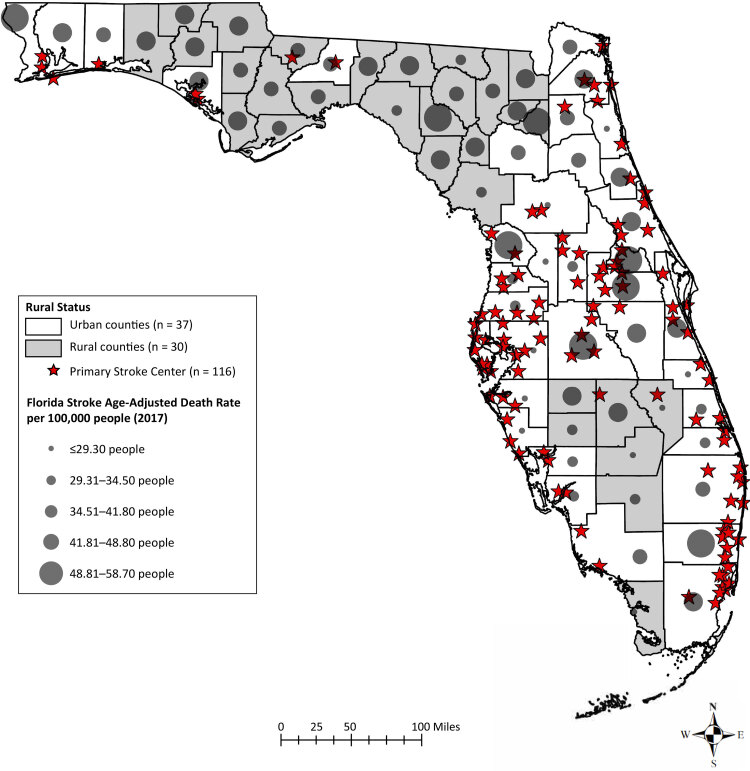
Static display of Florida’s distribution of rural versus urban and high versus low death rate, where stroke centers are in relation to urban versus rural and low versus high primary stroke centers, and age-adjusted stroke mortality rates, by quintile, in urban versus rural counties in 2017. Data sources: Florida’s Geospatial Open Data Portal 2017, 2018; Rural Health Information Hub 2017; US Census Bureau, 2010; Florida Geographic Data Library, 2012.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.