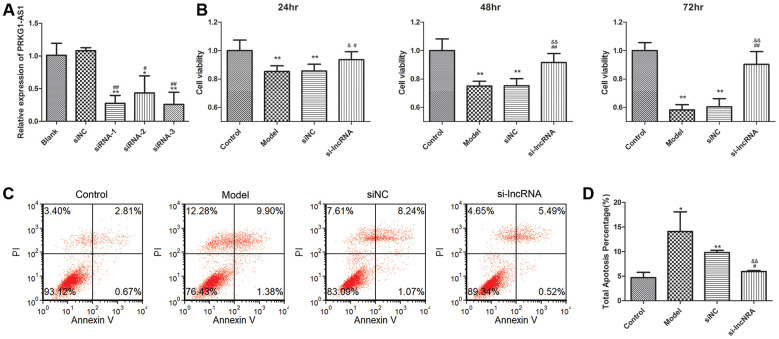
Figure 7.
The effect of knock-down of PRKG1-AS1 on cell viability and cell apoptosis. (A) PRKG1-AS1 was knocked down by small interference RNA (siRNA) and the efficiency was detected by qRT-PCR. Difference among groups was analyzed by ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 compared with blank group; # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01 compared with siNC (negative control) group. (B) Cell viability was tested by CCK-8 assay. Dexamethasone (15 mM) was added in human skeletal muscle myoblasts to establish atrophy cell model. Si-PRKG1-AS1 or siNC was transfected into human skeletal muscle myoblasts and incubated for 24 h, 48 h and 72 h. Cell viability was tested by CCK-8 assay. ** P < 0.01 compared with control group; # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01 compared with model group; & P < 0.05, && P < 0.01 compared with siNC group. (C) Cell apoptosis was tested by flow cytometry. Dexamethasone (15 mM) was added in human skeletal muscle myoblasts to establish atrophy cell model. Si-PRKG1-AS1 or siNC was transfected into human skeletal muscle myoblasts and incubated for 48 h. (D) Quantitative analysis of cell apoptosis. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 compared with control group; # P < 0.05 compared with model group; && P < 0.01 compared with siNC group.