Figure 1.
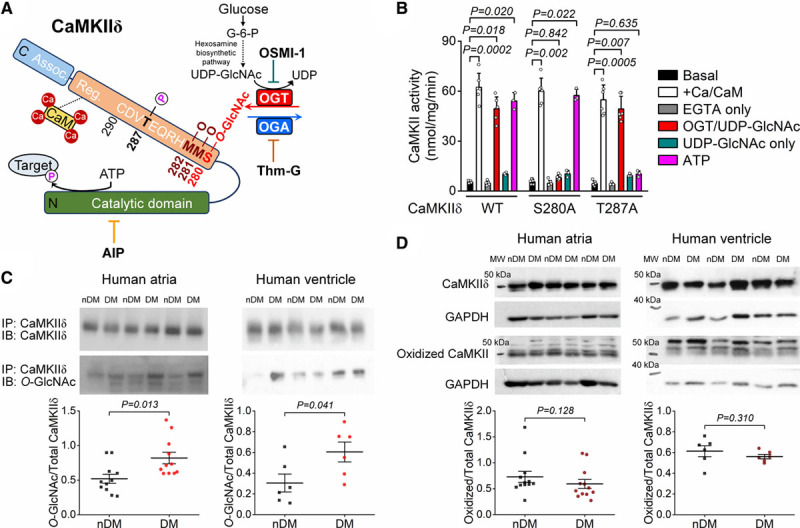
CaMKIIδ (Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II) O-GlcNAcylation is increased in human diabetic hearts. A, Schematic of CaMKIIδ structure and sequence of the regulatory hub domain and the O-GlcNAcylation pathway. B, CaMKII activity measured as 32P incorporation in HEK293 cell lysates expressing wild type (WT), S280A, and T287A CaMKIIδ (n, basal=6, Ca/CaM [calmodulin]=6, EGTA=6, OGT [O-GlcNAc transferase]/UDP-GlcNAc=6, UDP-GlcNAc=3, ATP=3 in all 3 CaMKIIδ forms). Kruskal-Wallis 1-way ANOVA, followed by Dunn multiple comparisons test. C, Western blot data showing enhanced CaMKII O-GlcNAcylation in human atrial and ventricular samples from diabetic (DM) vs nondiabetic (nDM) patients (n, atrial-DM=11, atrial-nDM=11, ventricular-DM=6, ventricular-nDM=6). Mann-Whitney test. D, CaMKII oxidation was not increased in atrial and ventricular samples from patients with diabetes (n, atrial-DM=12, atrial-nDM=12, ventricular-DM=6, ventricular-nDM=6). Mann-Whitney test. MW indicates molecular weight; OGA, O-GlcNAcase; and OSMI-1, αR-[[(1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-6-quinolinyl)sulfonyl]amino]-N-(2-furanylmethyl)-2-methoxy-N-(2-thienylmethyl)-benzeneacetamide.
