Figure 5.
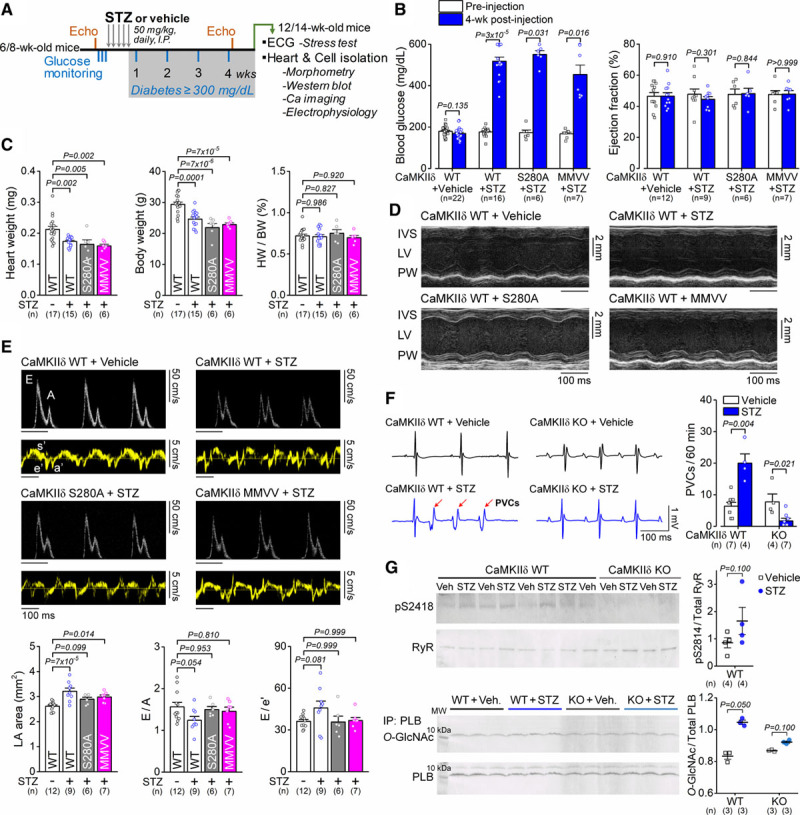
Diabetes-induced cardiac remodeling and arrhythmias are dependent on CaMKIIδ (Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II) activation. A, Study protocol of streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes and assessment of cardiac function. B, Blood glucose levels were highly elevated, whereas cardiac ejection fraction was preserved in STZ. Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test. C, Morphological parameters in either vehicle-treated or STZ-treated CaMKIIδ-wild type (WT), S280A, and mutated Met281Val and Met282Val (MMVV) mice. One-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnett multiple comparisons test. D, Preserved systolic heart function in STZ. E, Diastolic heart function (enlarged left atria, reduced E/A, increased E/e′) in 4-week diabetes. One-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnett multiple comparisons test. F, Incidence of premature ventricular complexes (PVCs) following isoproterenol+caffeine stress test was increased in diabetic WT animals, whereas CaMKIIδ-cardiac-specific knockout (cKO) was protective. Mann-Whitney test. G, Increased RyR (ryanodine receptor) S2814 phosphorylation and PLB (phospholamban) O-GlcNAcylation in STZ. Two technical replicates (blots) were performed for each protein sample. Mann-Whitney test. The number of biological replicates (n) is shown. HW/BW indicates heart weight to body weight ratio; IVS, interventricular septum; LA, left atrial; and LV, left ventricular.
