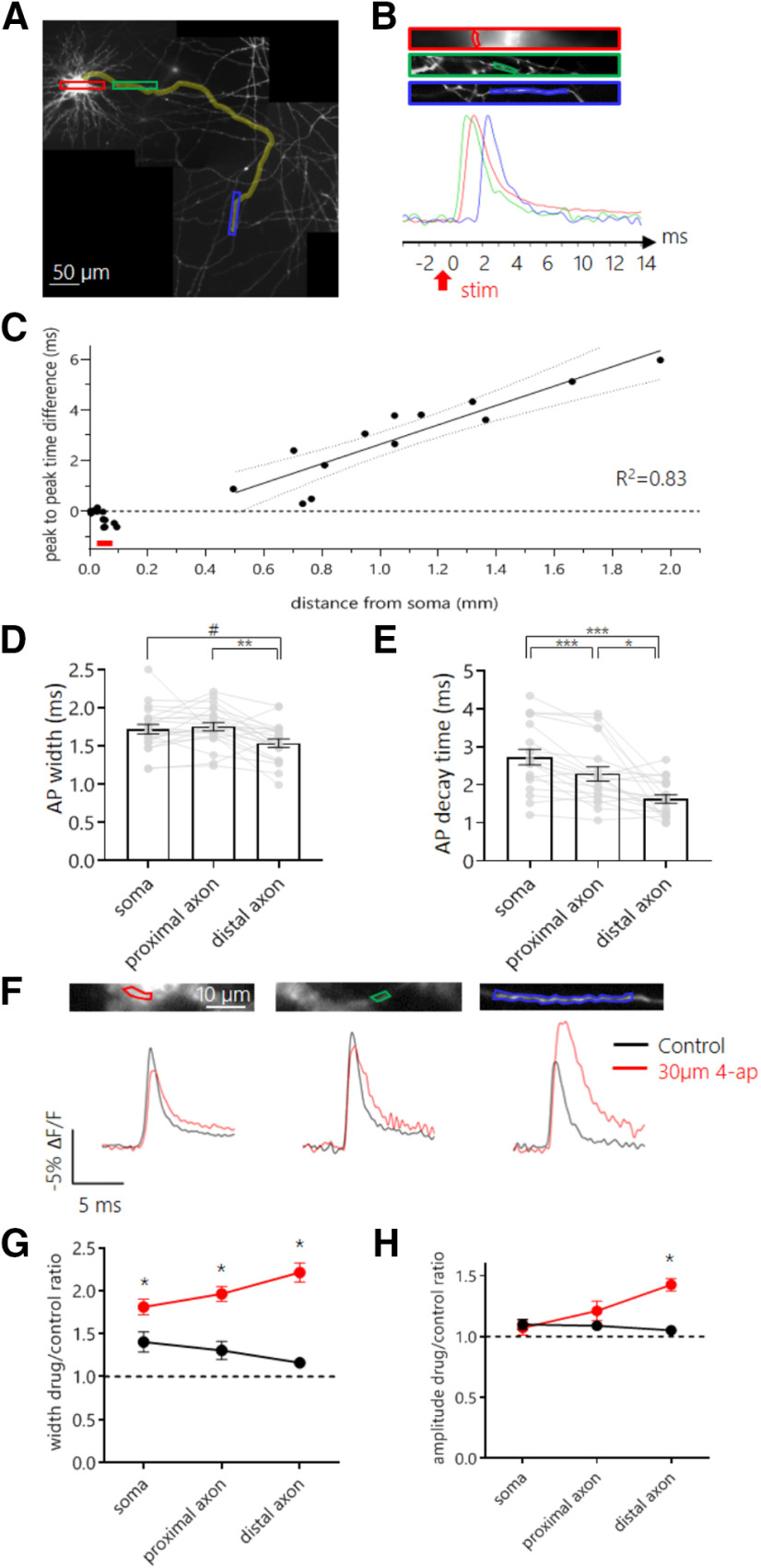
Figure 5.
Differential regulation of AP shape by Kv channels along different subcellular compartments. A, Reconstructed mosaic of fluorescent images of the axonal arbor of an example neuron expressing Ace-mNeon, acquired at 60× magnification. Neurons were stimulated locally with a bipolar electrode, and ROIs were chosen to include a portion of the somatic membrane, a proximal and a distal segment of the axon. Highlighted in yellow, the axonal path followed up to the most distal imaged fragment of the axon. Red, green, and blue rectangles indicate locations selected for imaging, enlarged in B. B, Imaged sections of the somatic membrane, a region of the axon proximal to the soma, and a region of the axon distal to the soma, respectively. The ROIs drawn around membrane fragments that were selected to extract the fluorescent profile in time are shown for each image. Bottom, overlaid averages of optical recordings of time-locked evoked APs extracted from ROIs containing the somatic membrane (red), the proximal axon (green) and the distal axon (blue). The red arrow indicates the time point of stimulation with the bipolar electrode. C, Time difference between the AP peaks recorded in the soma and in the axon plotted against the distance of the axon ROIs from the soma. Fit, linear regression performed with data from distal axon segments only. Red line indicates approximate location of the AIS. D, E, AP width (D) and 80−20% decay time (E) recorded at the three subcellular locations within the same set of cells. F, Average AP profile recorded with Ace-mNeon in the soma (top), proximal (middle), and distal (bottom) axon of the same cell. Traces shown for both the control condition (black) and after perfusion with 30 μm 4-ap (red). G, Quantification of the effect of 4-ap (red) and mock (black) perfusion on the AP width for soma, proximal, and distal axon. The width increases observed were 38% (CI = 6%, 70%), 62% (CI = 26%, 102%) and 95% (CI = 85%, 148%) with respect to mock treatment, respectively. H, Quantification of the effect of 4-ap (red) and mock (black) perfusion on the AP amplitude for soma, proximal, and distal axon. The amplitude increase observed in the distal axon was 32% (CI 27%, 57%) with respect to mock treatment. D, E, N = 19 cells, one-way repeated measures ANOVA with post hoc Tukey's multiple comparisons test. G, H, 4-ap, N = 8 cells; control, N = 4 cells; Mann–Whitney tests with Holm-Bonferroni correction; #p < 0.06, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.