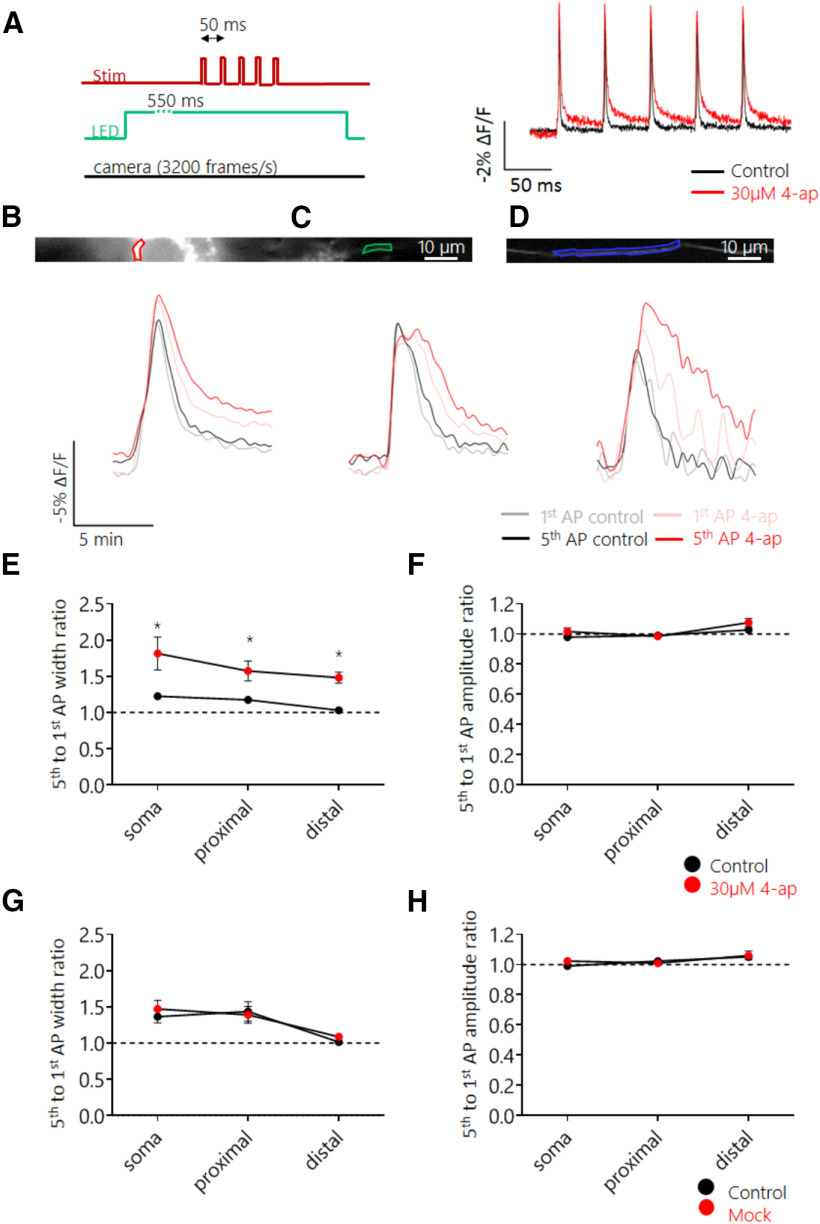
Figure 7.
Block of 4-ap-sensitive Kv channels increased AP broadening during 20 Hz trains across all subcellular compartments. A, Schematic representation of the experimental setup; five pulse stimulation trains were delivered with an ISI of 50 ms while subjecting the cell to continuous LED illumination and camera acquisition. Cells were recorded before and after addition of 30 μm 4-ap. B–D, Top, Example neuron expressing Ace-mNeon with selected ROIs in the soma (B), proximal (C), and distal axon segments (D). Bottom, overlaid average AP optic profiles of the first and fifth APs of the train before and after addition of 30 μm 4-ap for the respective ROIs. E, F, Quantification of the width (E) and amplitude (F) ratio between the fifth and first AP of the 20 Hz train in the three subcellular compartments, before and after addition of 30 μm 4-ap. AP width facilitation increased by 30.50% relative to the control recordings in the soma (CI= 10.70, 154.9%), by 28.87% in the proximal axon (CI = 2.0, 105.0%), and by 39.51% in the distal axon (CI = 11.47, 88.15%). G, H, Quantification of the width (G) and amplitude (H) ratio between the fifth and first AP of the 20 Hz train in the three subcellular compartments, before and after perfusion with mock (HBS without 4-ap). E, F, N = 8 cells; G, H, N = 4 cells. *p < 0.05; Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank tests with Holm–Bonferroni correction.