Figure 7.
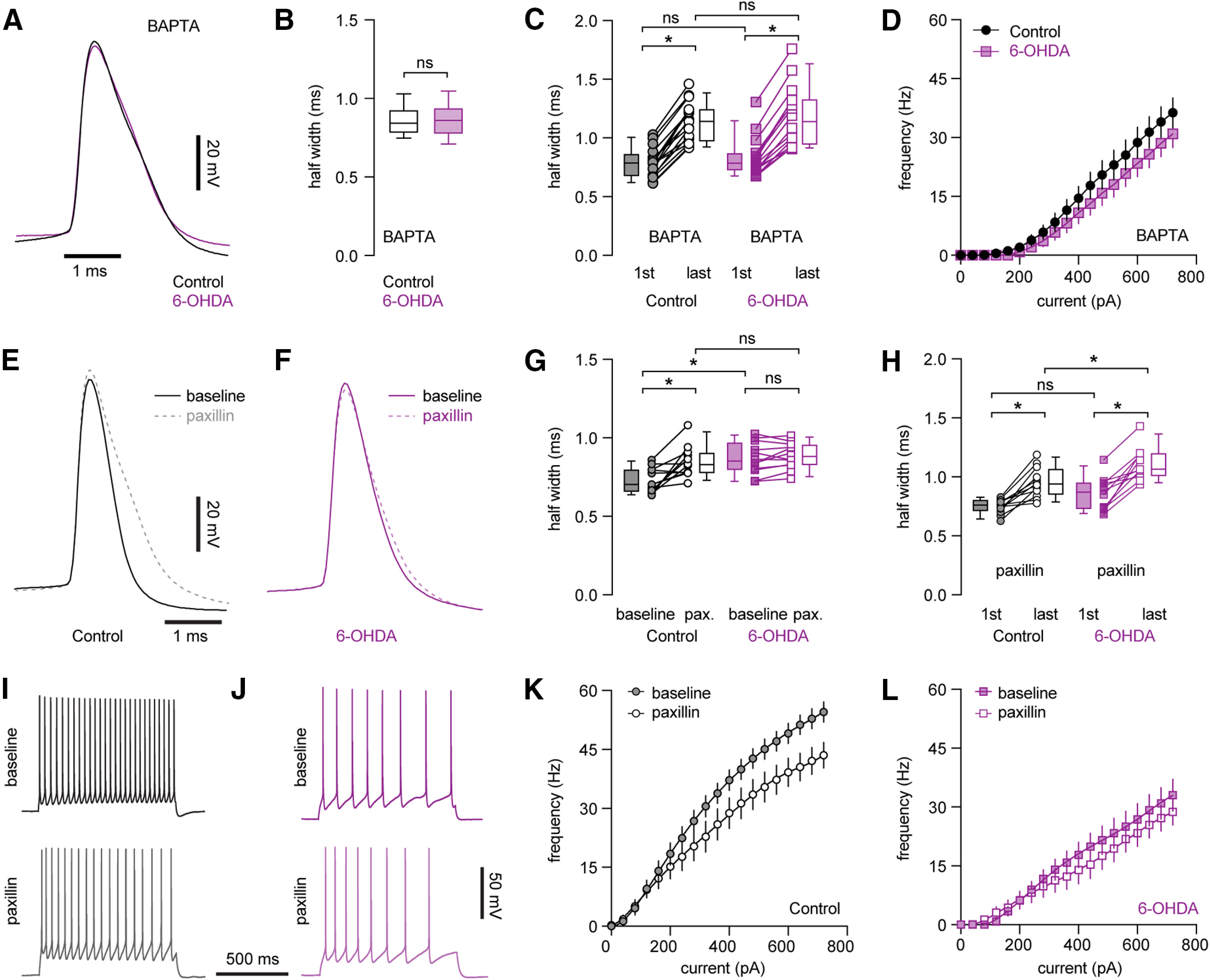
Decreased BK channel activity underlies AP broadening and impaired intrinsic excitability of PTNs following loss of midbrain DA neurons. A, Representative AP waveforms of PTNs from controls and 6-OHDA mice in the presence of BAPTA. APs were aligned at the threshold and overlaid for comparison. B, Box plot showing AP width of PTNs at rheobase from controls and 6-OHDA mice in the presence of BAPTA. C, Boxplot showing AP broadening during repetitive firing of PTNs in controls and 6-OHDA mice in the presence of BAPTA. D, Frequency-current curve of PTNs in controls and 6-OHDA mice in the presence of BAPTA. E, F, Representative AP waveforms at rheobase before and after paxillin application in PTNs from controls (E) and 6-OHDA mice (F). APs were aligned at the threshold and overlaid for comparison. G, Summarized graph showing paxillin broadened APs of PTNs from both controls and 6-OHDA mice. H, Summarized graph showing AP broadening during repetitive firing of PTNs from controls and 6-OHDA mice in the presence of paxillin. I, J, Representative AP traces of PTNs from controls and 6-OHDA mice in the absence and presence of paxillin. K, L, Frequency-current curves showing paxillin decreased the frequency of PTNs firing om controls, but not in 6-OHDA mice; *p < 0.05, ns, not significant, WSR or MWU tests.
