Fig. 3. Type 1 IFNs and cell death suppression are inversely associated with histone lactylation.
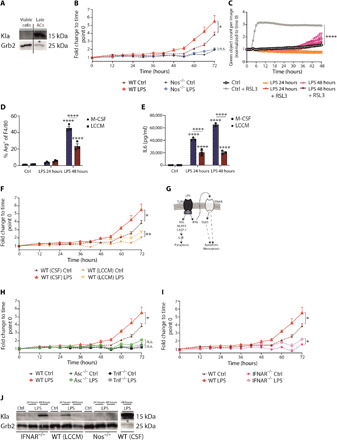
(A) Wild-type BMDMs were treated with LPS for 48 hours, and live/dead staining was used. Cells were sorted for viable cells and late apototic cells (ACs). (B) Wild-type and Nos2−/− BMDMs were left untreated (Ctrl) or were stimulated with LPS, and cell death was assayed by LDH release. (C) Wild-type BMDMs were left untreated or were stimulated with LPS, and where indicated, the ferroptosis inducer RSL3 was added. Cell death was detected via CellTox green cytotoxicity assay. (D) Wild-type BMDMs differentiated with macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) or LCCM were stimulated with LPS, and the percentages of Arg1+ of F4/80+ macrophages were determined. (E) The concentration of IL6 in the supernatant was measured by ELISA. (F) Wild-type BMDMs were differentiated with M-CSF or LCCM and stimulated with LPS. LDH release was evaluated over time. (G) Overview of LPS-induced cell death pathways. Wild-type, Asc−/−, and Trif−/− BMDMs (H) or Ifnar−/− BMDMs (I) were stimulated with LPS, and LDH release was evaluated. (J) Ifnar−/−, Nos2−/−, and wild-type BMDMs, differentiated with LCCM or CSF, were left untreated or were stimulated with LPS. * displays that increased cell death was observed. All values are means ± SEM; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001. Statistically significant differences were determined by a one-way (A, E, G, and H) or two-way (B to D) ANOVA with Bonferroni correction; n = 3 biological replicates. n.s., not significant.
