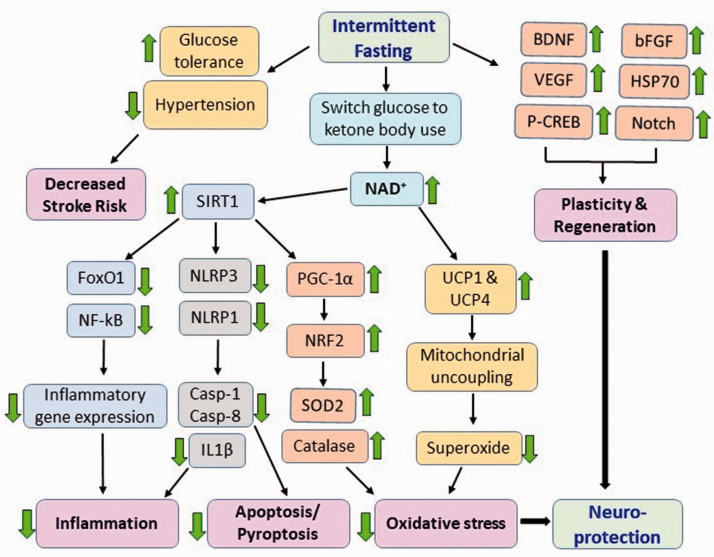
Figure 1.
Intermittent fasting (IF) influences the body by multiple mechanisms. IF increases glucose tolerance and controls blood pressure. This leads to better prognosis as diabetes and hypertension are major comorbid conditions for stroke. IF induces several genes that promote plasticity, regeneration and neuroprotection. IF also promotes the pathways that curtail inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis leading to neuroprotection after stroke.