Fig. 7. pDCs activated with CMV-infected cells facilitated NK cell activation.
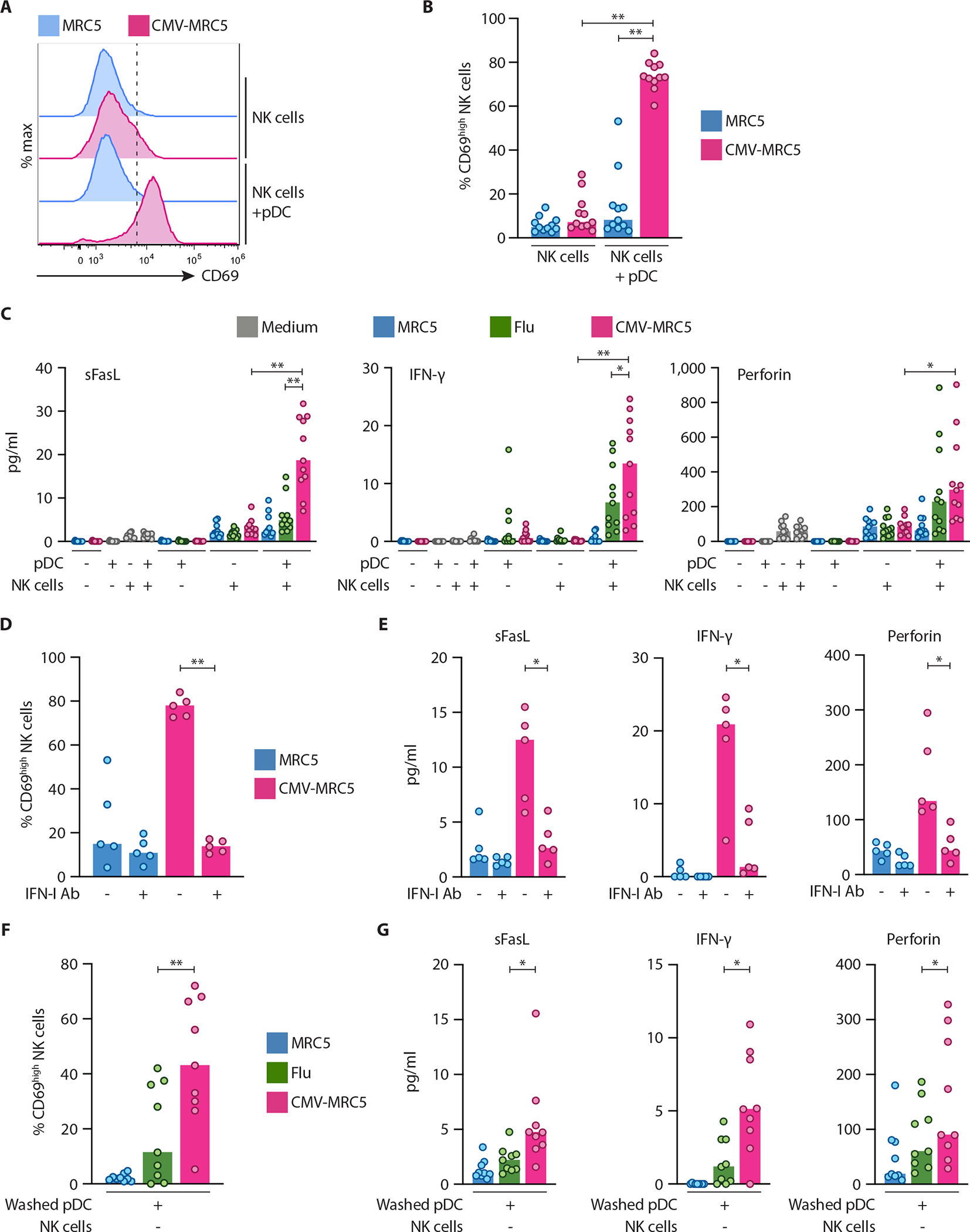
Human pDCs were enriched from donor PBMC, incubated in medium, with control MRC5 cells or with CMV-MRC5 or free Flu virus for 18 hours, and then cocultured with enriched NK cells directly (A to E) or after wash/live cell purification (F and G) for 60 hours.
(A–B) Representative histograms of CD69 expression on NK cells (A) and the fraction of CD69+ NK cells (B) after coculture with pDCs.
(C) NK cell-derived soluble factors in the supernatants of pDC-NK cell cocultures as determined by multiplex bead array.
(D–E) Percentage of CD69+ NK cells (D) and NK cell-derived soluble factors in the supernatants (E) in the absence or presence of IFN-I/IFNAR2 neutralizing antibody mixture (IFN-I Ab).
(F–G) Percentage of CD69+ NK cells (F) and NK cell-derived soluble factors in the supernatants (G) after coculture with washed/purified pDC.
In panels A–G, symbols indicate values from individual PBMC donors; bars indicate median.
