Figure 4.
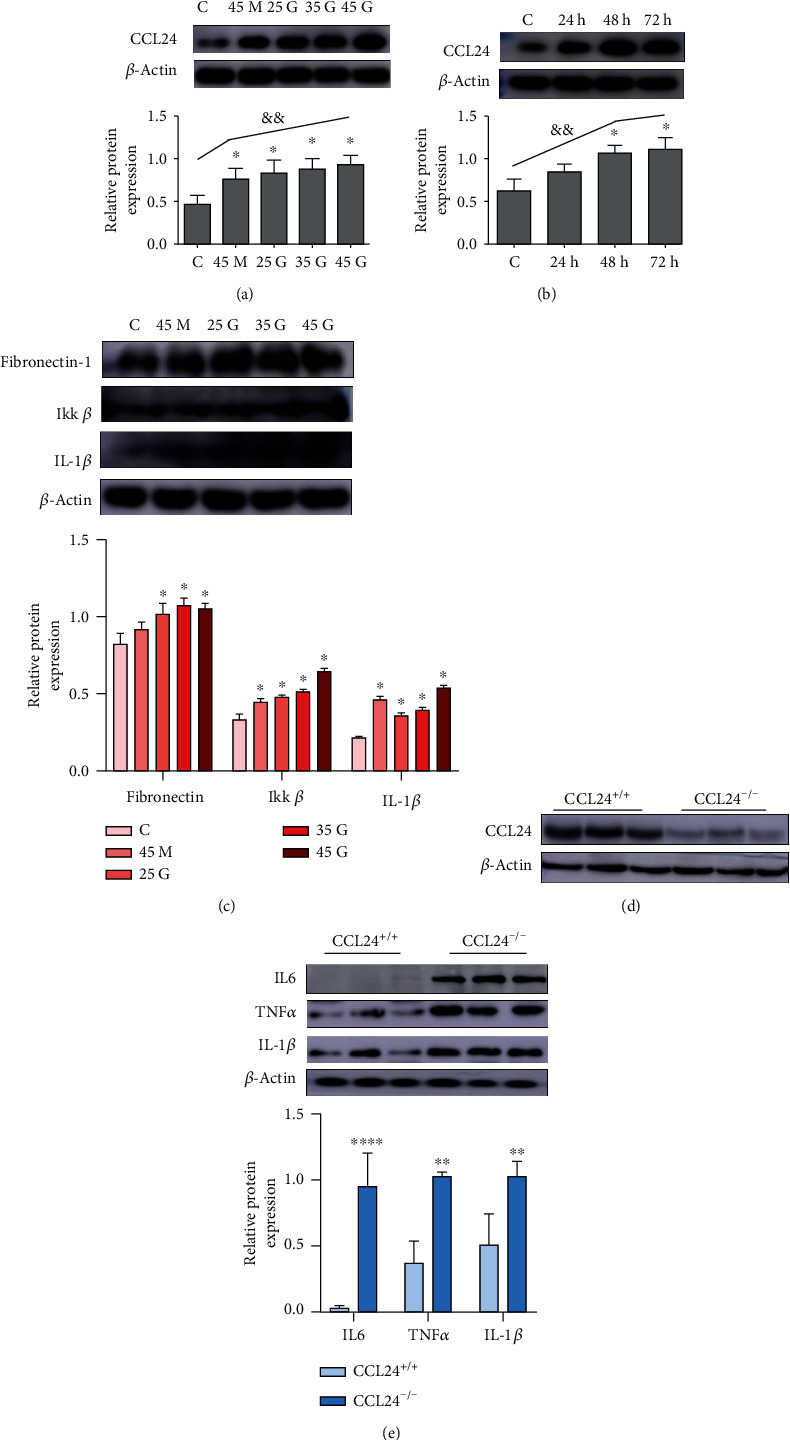
CCL24 is a potential protective factor for diabetic nephropathy by controlling inflammation in podocytes. The expression of CCL24 was positively correlated with (a) glucose concentration and (b) the duration of stimulation. (c) The level of fibrosis and the regulation of inflammatory regulatory pathways in the podocytes treated with high-glucose stimulation. (d) Molecular level detection after knockout of CCL24 gene by the CRISP-Cas 9 technology at podocyte level. (e) The changes of inflammatory pathways in CCL24−/− cell lines under high-glucose conditions (35 mmol/L D-glucose). C: the control of 5.5 mmol/L D-glucose, 45 M: 5.5 mmol glucose + mannitol 39.5 mmol, 25G: 25 mmol/L D-glucose, 35G: 35 mmol/L D-glucose, 45G: 45 mmol/L D-glucose. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 versus the control group (C) or CCL24+/+ group. &&p < 0.001, the time- and concentration-dependent variance trend test.
