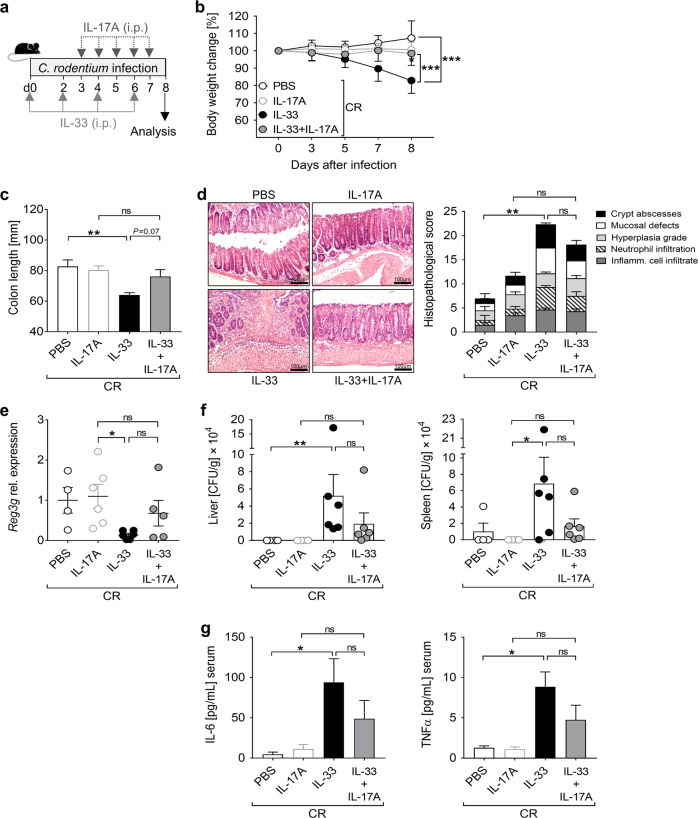
Fig. 7. IL-17A supplementation during infection compensates the detrimental effect of IL-33.
a CR-infected mice were treated with PBS (control group) or IL-33 as in Fig. 3a. Starting by day 3, one group of CR-infected IL-33-treated mice and one group of CR-infected non-treated mice received IL-17A daily until the end of the experiment. b Body weight changes during the course of infection are presented as percentage of initial weight on day 0. Statistical analyses were performed by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test. c Macroscopic score of colitis was assessed based on shortening of colon length. d Representative pictures (scale bars 100 µm) of H&E-stained colon sections (left) and histopathological score (right). e Reg3g mRNA expression in colon biopsies was determined by qRT-PCR and shown as fold change induction over PBS-treated group. f Systemic bacterial distribution upon IL-33 and/or IL-17A treatment was assessed on day 8 after infection in homogenized livers and spleens. g Serum cytokine levels were measured via Luminex technology. All data are presented as mean ± SEM and were pooled from two independent experiments (4–6 mice per group). Statistical analyses were performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test or Kruskal-Wallis test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.