Abstract
Objectives:
To train a deep learning model to differentiate between pathologically proven hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and non-HCC lesions on MRI including lesions with atypical imaging features.
Methods:
This IRB-approved retrospective study included 118 patients with 150 lesions (93(62%) HCC and 57(38%) non-HCC) pathologically confirmed through biopsies (n=72), resections (n=29), liver transplants (n=46), and autopsies (n=3). 47% of HCC lesions showed atypical imaging features (not meeting Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System [LI-RADS] criteria for definitive HCC/LR5). A 3D convolutional neural network (CNN) was trained on 140 lesions and tested for its ability to classify the 10 remaining lesions (5 HCC/5 non-HCC). Performance of the model was averaged over 150 runs with random sub-sampling to provide class-balanced test sets. A lesion grading system was developed to demonstrate the similarity between atypical HCC and non-HCC lesions prone to misclassification by the CNN.
Results:
The CNN demonstrated an overall accuracy of 87.3%. Sensitivities/specificities for HCC and non-HCC lesions were 92.7%/82.0% and 82.0%/92.7%, respectively. The area under the receiver operating curve was 0.912. CNN's performance was correlated with the lesion grading system, becoming less accurate the more atypical imaging features the lesions showed.
Conclusion:
This study provides proof-of-concept for CNN-based classification of both typical and atypical-appearing HCC lesions on multi-phasic MRI, utilizing pathologically confirmed lesions as “ground truth”.
Keywords: Carcinoma, Hepatocellular; Liver Neoplasms; Deep Learning; Magnetic Resonance Imaging; Neural Networks, Computer
1). Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the fourth most common cause of malignancy-related death worldwide, represents the most frequent primary liver cancer and its incidence rates continue to rise [1]. Other liver lesions to be differentiated include intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC), metastases as well as various types of benign lesions. Contrast-enhanced multi-phasic computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) play a central role for diagnosis and classification of these lesions. Standardized imaging features of HCC summarized in Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN) or Liver Reporting & Data System (LI-RADS) criteria provide the framework for clinical diagnostic workup [2, 3]. In lesions not meeting typical imaging criteria, the diagnosis can be challenging. High inter-reader variability depending on the radiologist’s experience may lead to unnecessary tissue biopsies [4] prone to complications such as hemorrhage, sepsis, carcinoid crisis [5] or tumor seeding [6]. These may compromise orthotopic liver transplantation which is the only established curative therapy for HCC [7, 8].
In recent years, deep learning has gained considerable traction in the field of medical image analysis. The most common tool to classify lesions on radiologic imaging is the convolutional neural network (CNN) [9]. Unlike other machine learning methods, CNNs do not require definition of specific radiological features to learn how to interpret images. After being shown imaging examples with and without the disease the CNN automatically learns features through backpropagation using multiple layers [10].
Recently, several studies used CNNs on CT/MRI focusing on liver lesions with typical appearances, allowing for distinctive image-based diagnosis according to the standardized criteria [11-13]. However, in order to be used in clinical management, CNNs should also correctly diagnose lesions that do not fit into established classification systems. As the number of heterogeneous input samples grows, CNNs have the potential to recognize atypical lesions, thus reducing the need for biopsies and subsequent post-biopsy complications.
The aim of this study was to prove the capability of CNNs to handle a wider spectrum of HCC and non-HCC lesions on multi-phasic contrast-enhanced MRI, using pathologically proven liver lesions as the “ground truth”.
2). Materials & Methods
This retrospective, single-center study was approved by the Institutional Review Board and Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). It was conducted according to the Standards for Report of Diagnostic Accuracy guidelines. Informed consent was waived.
Study Cohort Selection
HCC and non-HCC lesions from patients older than 18 years diagnosed between 2010 and 2018 were identified using a picture archiving and communication system (PACS) as well as the electronic medical record. Only patients with histopathological diagnosis were included. Pathological proof was established for all through biopsies (n=72), resections (n=29), liver transplants (n=46), and autopsies (n=3). In case of transplants/autopsies the liver was subject to gross pathological/histopathological analysis including full histological assessment of the HCC lesion. H&E staining was used to assess lesions and additional histopathological surface markers were applied. Lesions indicated in pathology reports were identified by a radiology trainee supervised by a board-certified radiologist sub-specialized in abdominal imaging with approximately 25 years of experience in body imaging. The lesions were qualified regarding size and intra-hepatic localization. A multi-phasic T1-weighted MRI data set including contrast-enhanced late arterial, portal venous and delayed/equilibrium phases had to be present to meet inclusion criteria. Clear correspondence between pathology and imaging was achieved collaboratively with a pathologist and side-by-side review of location for each tumor. If more than one lesion was visible on MRI in the segment described by the pathologist, images of CT- guided biopsy were used to ascertain the biopsied lesion. If these were unavailable, all lesions in the segment were excluded. Lesions that were biopsied before the MRI scan were excluded if procedure-related hemorrhage was leading to significant alteration of T1 signal. Up to 4 lesions per patient were used. In the non-HCC class, only primary liver neoplasms were included. HCC lesions with loco-regional therapy performed between MR imaging and resection/transplantation were included only if residual viable tumor was present on histology that would allow confirmation of etiology. Tumors with complete necrosis were excluded.
MRI Acquisition Protocol
MRI examinations were conducted on 1.5T or 3T MRI scanners including Signa Excite®, GE Discovery®, Siemens Aera®, Espree®, Verio®, Avanto®, Skyra®, and Trio Tim® scanners. Non-contrast T1 images were acquired in all patients prior to administration of intravenous contrast. After the administration of intravenous gadolinium-based contrast agent (including Gadavist® (Bayer), Dotarem® (Guerbet), Magnevist® (Bayer), ProHance® (Bracco Diagnostics), and Optimark® (Covidien), dosed at 0.1 mmol/kg), three T1-weighted three-dimensional (3D) gradient-echo (GRE) breath-hold imaging series (acquisition times of 12-18s, with fat suppression) were acquired reflecting CT/MRI LI-RADS recommendations: (1) late arterial, (2) portal venous and (3) delayed or equilibrium phase. Bolus tracking was applied in a large proportion of patients. Imaging parameters were in the range of TR 3-5 ms, TE 1-2 ms, flip angle 9-13 degrees, bandwidth 300-500 Hz, slice thickness 3-4 mm, image matrix 256 x 132 to 320 x 216, and field-of-view 300 x 200 mm to 500 x 400 mm. If a patient received multiple MRI scans, then the MRI performed closest to the date of pathological confirmation was used.
Image Processing
After MR imaging studies were retrieved from an institutional database, the x, y, and z coordinates of each lesion were manually recorded to define a 3D bounding box around the lesion (Figure 1). Only the image volume within this bounding box was analyzed by the model. Images were processed using code written in Python 3.5 (Python Software Foundation). Affine registration with a mutual information metric was used to register portal venous and delayed phase MRI sequences to the late arterial phase. The images were cropped to the bounding box defined above and normalized to an intensity range of −1 to 1 to reduce bias field effects. The images were further resampled to 36x36x12 voxels.
Figure 1:
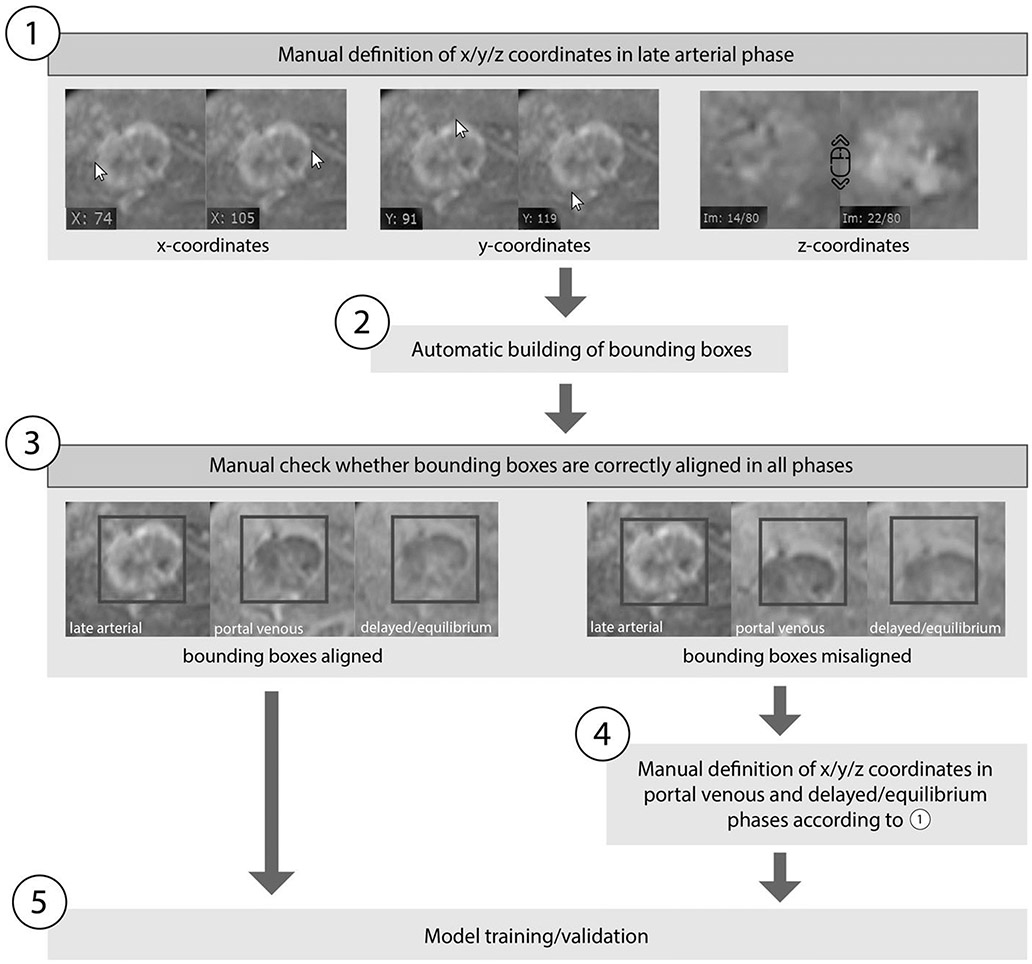
Determination of coordinates and bounding boxes. 1): All coordinates were determined manually in the late arterial phase using a DICOM viewer (Radiant®). The maximum extent of each lesion within an axis was determined using 2 coordinates. 2): Bounding boxes were automatically built according to the defined coordinates. 3): Bounding boxes were checked manually to ensure that they are aligned correctly in all phases. 4): In the few cases where the bounding boxes were misaligned due to breathing motion artefact, we manually specified the coordinates separately in portal venous and delayed/equilibrium phases according to step 1. 5): After all bounding boxes were correctly aligned, model training/validation was conducted according to figure 2.
To increase the number of training samples, the training set was augmented by a factor of 100 (n=14000) in standard fashion (Figure 2). Briefly, images were randomly rotated, shifted, scaled, flipped, shifted between phases, and scaled or shifted in intensity. This allows for the model to learn imaging features that are invariant to rotation or translation [14].
Figure 2:
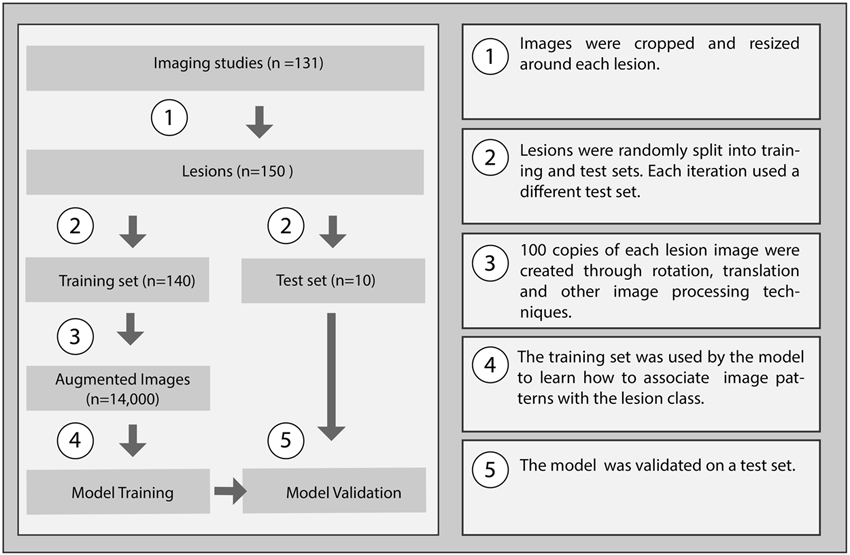
Flowchart of the lesion classification approach, including model training and testing.
Neural network architecture
The model was trained on a GeForce GTX 1060 (NVIDIA) graphics processing unit. It was built using Python 3.5 and Keras 2.2 (https://keras.io/) on a Tensorflow backend (Google, Mountain View, https://www.tensorflow.org/). The CNN consisted of three convolutional layers (64, 128, and 128 channels respectively; kernel size 3x3x2), two maximum pooling layers (size 2x2x2 and 2x2x1 respectively), and two fully connected layers (100 and 1 neurons respectively), with a sigmoid output corresponding to the probability of a lesion being HCC. The CNN used rectified linear units, batch normalization and 10% dropout.
Training and Evaluation
The CNN was trained on 70 HCC examples and 70 non-HCC examples, drawn randomly from the augmented dataset. An Adam optimizer was used with a minibatch size of 20 and learning rate of 0.01. The model was tested on its ability to correctly classify ten lesions in the test dataset, which was created by randomly selecting 5 HCC lesions and 5 non-HCC lesions. In total, 150 independent runs with different splits of training and test data sets (i.e. Monte Carlo cross-validation rather than k-fold cross-validation in order to balance HCC/non-HCC cases within each set) were used to estimate the model’s performance. This approach in conjunction with a 14:1 training:test ratio is consistent with machine learning best practice[15, 16].
Lesion Grading
As the dataset contained lesions with atypical appearances on MRI, a lesion grading system was developed based on the established LI-RADS major imaging criteria [17] using imaging features typical of HCC: arterial hyperenhancement, washout and enhancing rim/pseudocapsule (Figure 3). A supervised radiology trainee credited lesions 1 point for every applicable imaging feature so that a lesion could be graded on a scale of 0 to 3 points. According to this grading system, both HCC and non-HCC lesions were staged to demonstrate the similarity between HCC and non-HCC lesions prone to misclassification by the CNN. On the one hand, lesions receiving 3 points could either be typical LI-RADS applicable HCC or pathologically proven non-HCC lesions that presented like HCC on imaging. On the other hand, HCC lesions graded with 1 point showed atypical contrast dynamics with only one of these features. The differences of the grading scores between the well (>90% accuracy) and poorly (<90% accuracy) classified lesions were analyzed to provide possible explanations for misclassifications of lesions by the CNN.
Figure 3:
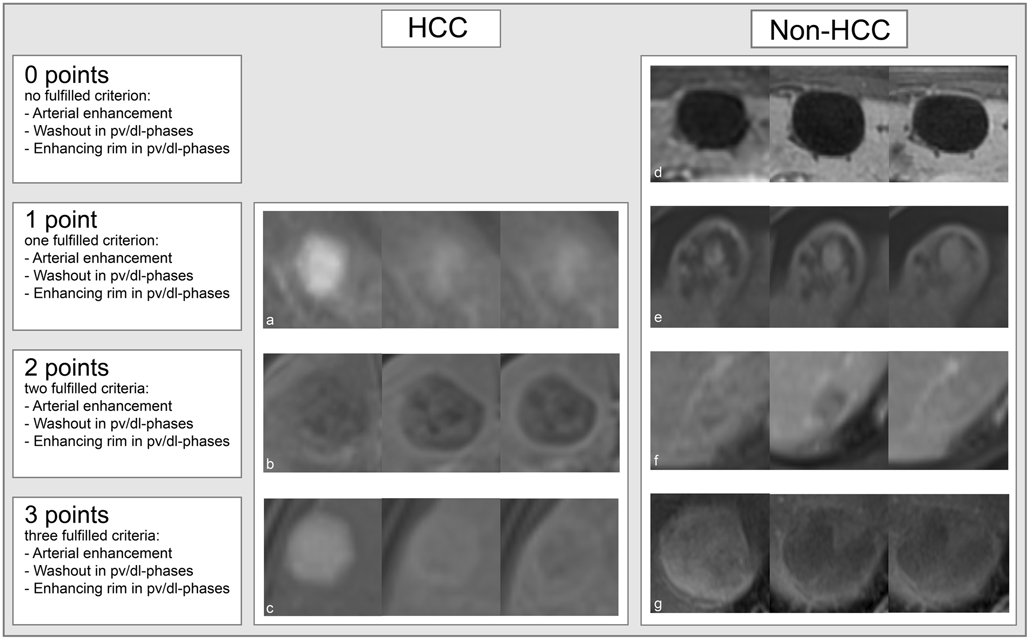
HCC as well as non-HCC lesions were graded with 0 to 3 points in order to demonstrate the similarity between HCC and non-HCC lesions prone to misclassification of lesions by the CNN. HCC = hepatocellular carcinoma. pv/dl = portal venous/delayed. a: HCC with arterial enhancement, b: HCC with washout and enhancing rim, c: HCC with arterial enhancement, washout and enhancing rim, d: cyst with no fulfilled criterion, e: hemangioma with enhancing rim, f: hemangioma with enhancing rim and washout, g: cyst with arterial enhancement, washout and enhancing rim.
Statistics
Sensitivity, specificity, and overall accuracy were calculated in order to validate the performance of the deep learning model. These metrics were averaged over 150 runs with random sub-sampling to yield class-balanced test sets. The receiver operating characteristic curve was obtained and the area under the curve (AUC) was calculated (Figure 4).
Figure 4:
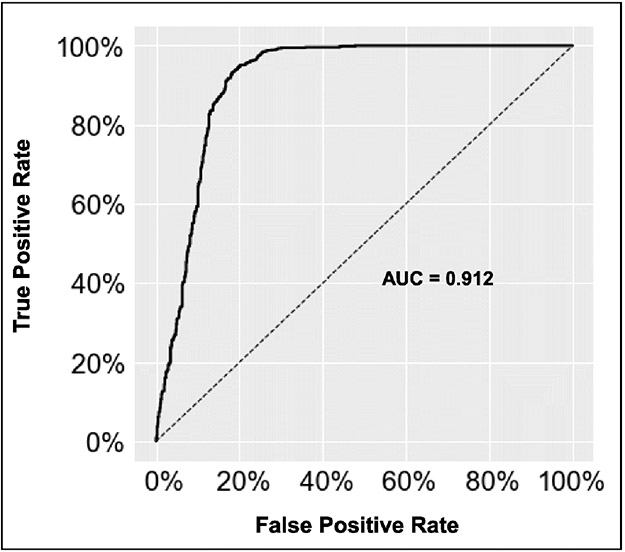
Model receiver operating characteristic curve for distinguishing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) from non-HCC lesions. AUC = area under the curve.
3). Results
Study population
This study included 118 patients with HCC (n=73, 62%) and non-HCC lesions (n=45, 38%). The HCC cohort contained 57 (78%) men and 16 (22%) women, whereas 23 (51%) men and 22 (49%) women were included in the non-HCC cohort. The mean age of the HCC patients was 61±8 (mean, standard deviation) and the mean age of the non-HCC patients was 59±13 years. The cohort contained 87 patients with cirrhosis, including 73 (84%) in the HCC class and 14 (16%) in the non-HCC class. The majority of these patients were classified as Child-Turcotte-Pugh-Score A (n=50, 57%) and the most common etiology was hepatitis C infection (n=61, 59%). The median Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score for all patients was 9. The exact values can be obtained in Table 1.
Table 1: Patient characteristics.
The numerical data are summarized as mean ± standard deviation or median (*) and the categorical data are shown as frequency (percentage). HCC = hepatocellular carcinoma, ICC = intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, FNH = focal nodular hyperplasia, MELD = Model For End-Stage Liver Disease, Child-Pugh= Child-Turcotte-Pugh-Score, NASH= nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, PSC = primary sclerosing cholangitis, ECOG = Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group, BCLC = Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer, HKLC = Hong Kong Liver Cancer classification system.
| HCC | Non-HCC | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICC | Regenerative nodule |
Dysplastic nodule |
Hemangioma | Cyst | FNH | Bile duct adenoma |
||
| Number of Patients | 73 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 16 | 10 | 2 | 1 |
| Gender | ||||||||
| - Male | 57 (78) | 9 (75) | 1 (50) | 1 (50) | 7 (44) | 3 (30) | 1 (50) | 1 (100) |
| - Female | 16 (22) | 3 (25) | 1 (50) | 1 (50) | 9 (56) | 7 (70) | 1 (50) | 0 (0) |
| Age at imaging | 61±8 | 69±13 | 37* | 61* | 57±10 | 56±9 | 42* | 53* |
| Ethnic | ||||||||
| - Caucasian | 53 (73) | 9 (75) | 1 (50) | 2 (100) | 11 (69) | 8 (80) | 1 (50) | 1 (100) |
| - African American | 9 (12) | 2 (17) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (13) | 0 (0) | 1 (50) | 0 (0) |
| - Asian | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| - Other | 10 (14) | 1 (8) | 1 (50) | 0 (0) | 3 (19) | 2 (20) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| MELD | 10* | 13±6 | 20* | 10* | 8±2 | 6* | 10* | 10* |
| Cirrhosis | 73 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| - Child-Pugh | ||||||||
| ∘ A | 44 (60) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (50) | 4 (67) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (100) |
| ∘ B | 26 (36) | 1 (100) | 1 (50) | 1 (50) | 2 (33) | 2 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| ∘ C | 3 (4) | 0 (0) | 1 (50) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| - Cause | ||||||||
| ∘ Hepatitis B | 2 (3) | 0 (0) | 1 (50) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| ∘ Hepatitis C | 53 (62) | 1 (50) | 0 (0) | 2 (100) | 2 (33) | 2 (100) | 0 (0) | 1 (100) |
| ∘ Alcohol | 21 (25) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (50) | 2 (33) | 1 (50) | 1 (100) | 0 (0) |
| ∘ NASH | 8 (9) | 0 (0) | 1 (50) | 0 (0) | 1 (17) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (100) |
| ∘ PSC | 1(1) | 1 (50) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (17) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Malignancy related | ||||||||
| - ECOG | ||||||||
| ∘ 0 | 55 (75) | 3 (25) | ||||||
| ∘ 1 | 16 (22) | 4 (33) | ||||||
| ∘ 2 | 1 (1) | 2 (17) | ||||||
| ∘ 3 | 1 (1) | 1 (8) | ||||||
| ∘ unknown | 0 (0) | 2 (17) | ||||||
| - Extrahepatic Spread | 1 (14) | 0 (0) | ||||||
| HCC related | ||||||||
| - BCLC | ||||||||
| ∘ 0 | 12 (16) | |||||||
| ∘ A | 45 (62) | |||||||
| ∘ B | 0 (0) | |||||||
| ∘ C | 13 (18) | |||||||
| ∘ D | 3 (4) | |||||||
| - HKLC | ||||||||
| ∘ 1 | 43 (58) | |||||||
| ∘ 2 | 26 (36) | |||||||
| ∘ 3 | 1 (1) | |||||||
| ∘ 4 | 0 (0) | |||||||
| ∘ 5 | 3 (4) | |||||||
A total of 93 (62%) HCC lesions and 57 (38%) non-HCC lesions were analyzed. The non-HCC group consisted of 19 (33%) ICCs, 16 (28%) hemangiomas, 15 (26%) cysts, 2 (4%) regenerative nodules, 2 (4%) dysplastic nodules, 2 (4%) FNHs and 1 (2%) bile duct adenoma.
The median diameter for all lesions was 2,3cm. The median timeframe between the MRI study and pathological proof was 1.6 months (range, 0-25 months) for HCC lesions if imaging was obtained prior to the pathological confirmation. Imaging after pathological confirmation was performed within one day. For non-HCC lesions, the median time between the MRI study and pathological confirmation was 1.4 months (range, 0-73 months), if imaging was obtained prior to the pathological confirmation. Imaging after pathological confirmation was performed within a median time of 5.5 months (0-24 months) (Table 2). One to four lesions per patient (median=1) and one to three lesions per imaging set (median=1) were included (Table 3).
Table 2: Lesion characteristics.
The numerical data are summarized as mean ± standard deviation or median(*) and the categorical data are shown as frequency (percentage). HCC = hepatocellular carcinoma, ICC = intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, FNH = focal nodular hyperplasia, TACE = transcatheter arterial chemoembolization, MWA = microwave ablation, RFA = radiofrequency ablation
| HCC | Non-HCC | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICC | Regenerative nodule |
Dysplastic nodule |
Hemangioma | Cyst | FNH | Bile duct adenoma |
||
| Number of Lesions | 93 | 19 | 2 | 2 | 16 | 15 | 2 | 1 |
| Pathological proof | ||||||||
| - Biopsy | 47 (50) | 15 (79) | 1 (50) | 1 (50) | 6 (37) | 0 (0) | 2 (100) | 0 (0) |
| - Resection | 10 (11) | 4 (21) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 5 (31) | 10 (67) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| - Explant | 36 (39) | 0 (0) | 1 (50) | 1 (50) | 3 (19) | 4 (27) | 0 (0) | 1 (100) |
| - Autopsy | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (13) | 1 (7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Cirrhosis | 93 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 0 | 1 |
| Timeframe in days (median) | ||||||||
| - Imaging pre path | 49 | 22 | 42 | 68 | 104 | 181 | 509 | 27 |
| - Imaging post path | 1 | 295 | 0 | 0 | 143 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Diameter in cm | 2,0* | 4.2±1.4 | 3,7* | 1.1* | 5.0±4.0 | 4.9±3.5 | 4,46* | 1.4* |
| Residual tumor | 8 | 0 | ||||||
| Treatments | 29 | 0 | ||||||
| - TACE | 22 (76) | |||||||
| - Bland embolization | 3 (10) | |||||||
| - Ethanol ablation | 2 (7) | |||||||
| - MWA | 6 (21) | |||||||
| - RFA | 3 (10) | |||||||
| LI-RADS | ||||||||
| - LR5 | 49 (53) | |||||||
| - < LR5 | 44 (47) | |||||||
Table 3: Image characteristics.
HCC = hepatocellular carcinoma, ICC = intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, FNH = focal nodular hyperplasia.
| HCC | Non-HCC | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICC | Regenerative nodule |
Dysplastic nodule |
Hemangioma | Cyst | FNH | Bile duct adenoma | ||
| Number of Patients | 73 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 16 | 10 | 2 | 1 |
| Number of Imaging Studies | 80 | 17 | 2 | 2 | 16 | 11 | 2 | 1 |
| Number of Lesions | 93 | 19 | 2 | 2 | 16 | 15 | 2 | 1 |
Deep Learning Model Performance
The deep learning model demonstrated a training accuracy of 94.1% ± 2.0 (19766/21000 volumetric samples). The performance was validated on a test set after 30 iterations, where the CNN demonstrated an overall accuracy of 87.3% ± 10.5 (1310/1500). The sensitivity to classify HCC and the non-HCC class was 92.7% and 82.0%, respectively, and the specificity for HCC and the non-HCC class was 82.0% and 92.7%, respectively (Table 4). The receiver operating characteristic curve demonstrated an AUC of 0.912 (Figure 4). The CNN was trained in 3.2 minutes ± 0.9, and the computing time to classify each lesion in the test data set was 2.9 milliseconds ± 1.7.
Table 4: Performance of the neural network on HCC classification.
Performance was averaged over 150 runs with random sub-sampling to yield class-balanced test sets. HCC = hepatocellular carcinoma.
| HCC | Non-HCC | Overall | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Training lesions | 88 | 52 | 140 |
| Test lesions | 5 | 5 | 10 |
| Sensitivity | 92.7% | 82.0% | 87.3% |
| Specificity | 82.0% | 92.7% | 87.3% |
Evaluation of Lesion Grading
According to the grading system, 23 (25%) of the HCC lesions were scored with 1 point, 28 (30%) with 2 points, and 42 (45%) with 3 points (Figure 5). In the non-HCC class, 16 (28%) lesions were scored with 0, 24 (42%) with 1, 11 (19%) with 2, and 6 (11%) with 3 points. The Kruskal-Wallis test showed a significant positive correlation of the grading score with improved classification accuracy in HCC lesions (p=0.012) and reduced classification accuracy in non-HCCs (p < .001). Specifically, in the HCC class, 1 of 42 (2%) lesions graded with 3 points, 4 of 28 (14%) lesions with 2 points and 5 of 23 (22%) lesions graded with 1 point were poorly classified (≤90% accuracy in 150 runs) by the CNN. The one poorly classified 3 point HCC lesion as well as 3 of 4 poorly classified 2 point HCC lesions showed poor image quality. Moreover, 2 of the 4 poorly classified 2 point HCC lesions were in close proximity to the liver margin. In the non-HCC class, none of the lesions with 0 points, 2 of 24 (8%) lesions graded with 1 point, 3 of 11 (27%) lesions with 2 points and 6 of 6 (100%) lesions graded with 3 points 100% (6/6) were poorly classified.
Figure 5:
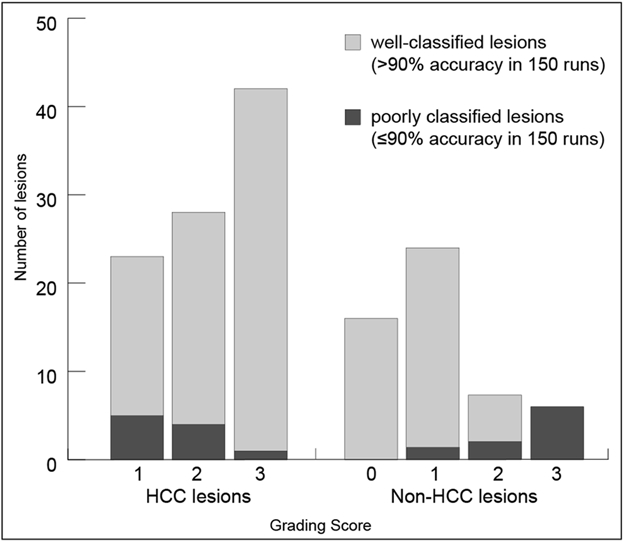
Number of lesions by grading score. HCC = hepatocellular carcinoma.
4). Discussion
This study demonstrates a histopathologically validated deep learning approach to differentiate between HCC and non-HCC lesions on multi-phasic contrast-enhanced MRI. The model achieved an overall accuracy of 87.3%, with high sensitivity (92.7%) and moderate specificity (82.0%) for HCC. The CNN’s short computation time could allow for practical integration into a radiologist’s workflow without producing delays.
A few recent studies have focused on classifying different types of liver lesions using a deep learning approach. A previous study [11] utilized a CNN trained to differentiate between six different types of liver lesions with an overall accuracy of approximately 90%. This proof-of-concept study only used lesions with typical imaging features. However, inclusion of atypical lesions may provide a more representative dataset and increased translatability to clinical practice. Another study investigating deep learning-based liver tumor classification also included atypical/indeterminate lesions. However, all indeterminate lesions were grouped into one class without further sub-classification [13]. The CNN developed in the current study was trained on a majority of atypical lesions to further classify those lesions as HCC or non-HCC as verified by pathology. This binary differentiation is a significant step towards classifying indeterminant lesions non-invasively in clinical practice. The decision HCC vs. non-HCC is particularly important since HCC is a malignant disease which can be treated curatively if diagnosed early. Moreover, the aforementioned study was based on CT whereas the current study utilized MRI, providing a wider variety of imaging features for the CNN to capture. In the present study, 47% of HCC lesions did not meet LI-RADS criteria for definitive HCC (LR5) and 48% of all lesions were biopsied, generally suggesting indeterminate appearance on imaging. A grading system was used to evaluate the representation of atypical-appearing lesions, assigning one point for each classical imaging feature of HCC (arterial hyperenhancement, washout, and pseudocapsule). According to this grading system, 25% of the HCC lesions scored one point because of their atypical appearances, and 30% of non-HCC lesions scored two or more points, mimicking typical appearances of HCC lesions. While the present study showed a slightly lower overall accuracy than the previous study with classical-appearing lesions, the results suggest that a CNN model trained with pathologically-proven atypical lesions can still provide relatively high accuracy.
Classical-appearing lesions generally demonstrated higher classification accuracy. The lower specificity of HCC classification is likely related to non-HCC lesions displaying features of HCC on imaging. However, a small number of HCC lesions graded with 2 and 3 points were poorly classified, possibly caused by poor image quality or lesions in close proximity to the liver margin. The seemingly high standard deviation is a consequence of the number of validation images in each fold. Vanilla CNNs were considered appropriate for the small cropped 3D images in our study, as sophisticated architectures such as ResNet [18] and DenseNet [19] are designed for larger datasets and 2D high resolution images.
This study has several limitations. A relatively small cohort was used due to the single center nature and the requirement for histopathological reference standard. Because the majority of non-HCC lesions in the liver were benign and did not require surgical therapy fewer pathological proven non-HCCs than HCCs were available with ground-truth pathological proof and were mostly acquired incidentally in the setting of transplantation for liver failure or accompanied by secondary HCC in the liver. Therefore, these non-HCC lesions were grouped into a single pooled category. Metastatic lesions were excluded because pathology proof is frequently unavailable for secondary malignancies which do not generally undergo surgical resection. Pathological confirmation from various sources was used, including biopsies, resections, explants, and autopsies. Additionally, the time interval between MRI and pathological confirmation was variable and, especially in benign lesions, relatively large. However, the probability of a malignant transformation for a definitively benign finding is exceedingly low [20]. Additionally, the time interval in this study was less relevant, since pathology was only used to provide proof of diagnosis. Due to the small sample size, a large number of non-HCC lesions without background cirrhosis were used. However, lesions were cropped which reduced the impact of background liver tissue on the image analysis. Moreover, using heterogenous imaging sources may seem like a limiting factor, but demonstrates the robustness of the CNN in the setting of different MRI scanners and acquisition protocols. The algorithm does not account for variabilities in contrast agents/ acquisition time/ image quality, suggesting that prospective studies should validate those points. Additionally, the diagnostic performance of CNN vs. non-assisted radiologist vs. CNN-assisted radiologist should be investigated in future studies in order to proof the CNN’s clinical applicability. Moreover, lesion grading was conducted by single human reader leading to possible bias, which we tried to minimize through supervision.
In conclusion, this study demonstrates the use of deep learning for classification of both typical and atypical-appearing HCC lesions on multi-phasic MRI, utilizing pathologically confirmed lesions as “ground truth”. Currently most deep learning tools do not provide radiological-pathological validation in their training dataset. By strictly including only pathologically confirmed lesions, the underlying biological validity of deep learning systems can be optimized, paving the way for integration of decision support tools in clinical practice. Moreover, this allows for the evaluation of lesions with more atypical appearances, pushing the boundaries of non-invasive imaging-based diagnosis. In this manner, CNNs have the potential to eventually reduce the need for biopsies and their associated complications, resulting in improved patient care. The short computing time of our CNN will facilitate the inclusion into clinical routine.
Key points:
A CNN trained on atypical appearing pathologically proven HCC lesions not meeting LI-RADS criteria for definitive HCC (LR5) can correctly differentiate HCC lesions from other liver malignancies, potentially expanding the role of image-based diagnosis in primary liver cancer with atypical features.
The trained CNN demonstrated an overall accuracy of 87.3% and a computational time of < 3 ms which paves the way for clinical application as a decision support instrument.
1.
Funding
CW received funding from the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA Research Resident Grant #RR1731). JD, JC, ML, and CW received funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH/NCI R01 CA206180).
Abbreviations:
- AUC
Area under the curve
- CNN
Convolutional neural network
- FNH
Focal nodular hyperplasia
- HCC
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- HIPAA
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
- ICC
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- LI-RADS
Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System
- MELD
Model for End-Stage Liver Disease
- NPV
Negative predictive value
- PACS
Picture Archiving and Communication system
- PPV
Positive predictive value
Footnotes
Guarantor:
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Dr. Julius Chapiro, MD, PhD.
Conflict of Interest:
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Statistics and Biometry:
No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper.
Informed Consent:
Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board.
Ethical Approval:
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Study subjects or cohorts overlap:
No overlap in study cohorts
Methodology
Methodology:
• retrospective
• diagnostic study
• performed at one institution
References
- 1.Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 68:394–424. 10.3322/caac.21492 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wald C, Russo MW, Heimbach JK, et al. (2013) New OPTN/UNOS Policy for Liver Transplant Allocation: Standardization of Liver Imaging, Diagnosis, Classification, and Reporting of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Radiology 266:376–382. 10.1148/radiol.12121698 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.CT/MRI LI-RADS v2018. https://www.acr.org/Clinical-Resources/Reporting-and-Data-Systems/LI-RADS/CT-MRI-LI-RADS-v2018. Accessed 31 Aug 2020
- 4.Davenport MS, Khalatbari S, Liu PSC, et al. (2014) Repeatability of Diagnostic Features and Scoring Systems for Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Using MR Imaging. Radiology 272:132–142. 10.1148/radiol.14131963 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Smith EH (1991) Complications of percutaneous abdominal fine-needle biopsy. Review. Radiology 178:253–258. 10.1148/radiology.178.1.1984314 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Seehofer D, Öllinger R, Denecke T, et al. (2017) Blood Transfusions and Tumor Biopsy May Increase HCC Recurrence Rates after Liver Transplantation. J Transplant 2017:. 10.1155/2017/9731095 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Quaia E, De Paoli L, Angileri R, et al. (2014) Indeterminate solid hepatic lesions identified on non-diagnostic contrast-enhanced computed tomography: Assessment of the additional diagnostic value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the non-cirrhotic liver. European Journal of Radiology 83:456–462. 10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.12.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pérez Saborido B, Menéu Díaz JC, Jiménez de los Galanes S, et al. (2005) Does Preoperative Fine Needle Aspiration-Biopsy Produce Tumor Recurrence in Patients Following Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma? Transplantation Proceedings 37:3874–3877. 10.1016/j.transproceed.2005.09.169 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Yamashita R, Nishio M, Do RKG, Togashi K (2018) Convolutional neural networks: an overview and application in radiology. Insights into Imaging. 10.1007/s13244-018-0639-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Greenspan H, van Ginneken B, Summers RM (2016) Guest Editorial Deep Learning in Medical Imaging: Overview and Future Promise of an Exciting New Technique. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 35:1153–1159. 10.1109/TMI.2016.2553401 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hamm CA, Wang CJ, Savic LJ, et al. (2019) Deep learning for liver tumor diagnosis part I: development of a convolutional neural network classifier for multi-phasic MRI. Eur Radiol. 10.1007/s00330-019-06205-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wang CJ, Hamm CA, Savic LJ, et al. (2019) Deep learning for liver tumor diagnosis part II: convolutional neural network interpretation using radiologic imaging features. Eur Radiol 29:3348–3357. 10.1007/s00330-019-06214-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yasaka K, Akai H, Abe O, Kiryu S (2018) Deep Learning with Convolutional Neural Network for Differentiation of Liver Masses at Dynamic Contrast-enhanced CT: A Preliminary Study. Radiology 286:887–896. 10.1148/radiol.2017170706 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2017) ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Communications of the ACM 60:84–90. 10.1145/3065386 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Erickson BJ, Korfiatis P, Akkus Z, Kline TL (2017) Machine Learning for Medical Imaging. Radiographics 37:505–515. 10.1148/rg.2017160130 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Arlot S, Celisse A (2010) A survey of cross-validation procedures for model selection. Statist Surv 4:40–79. 10.1214/09-SS054 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.CT/MRI LI-RADS v2017. https://www.acr.org/Clinical-Resources/Reporting-and-Data-Systems/LI-RADS/CT-MRI-LI-RADS-v2017. Accessed 17 May 2018
- 18.He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2015) Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. arXiv:151203385 [cs] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Huang G, Liu Z, van der Maaten L, Weinberger KQ (2018) Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. arXiv:160806993 [cs] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fodor M, Primavesi F, Braunwarth E, et al. (2018) Indications for liver surgery in benign tumours. Eur Surg 50:125–131. 10.1007/s10353-018-0536-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


