Figure 4. IRTKS is enriched in puncta that give rise to new microvilli.
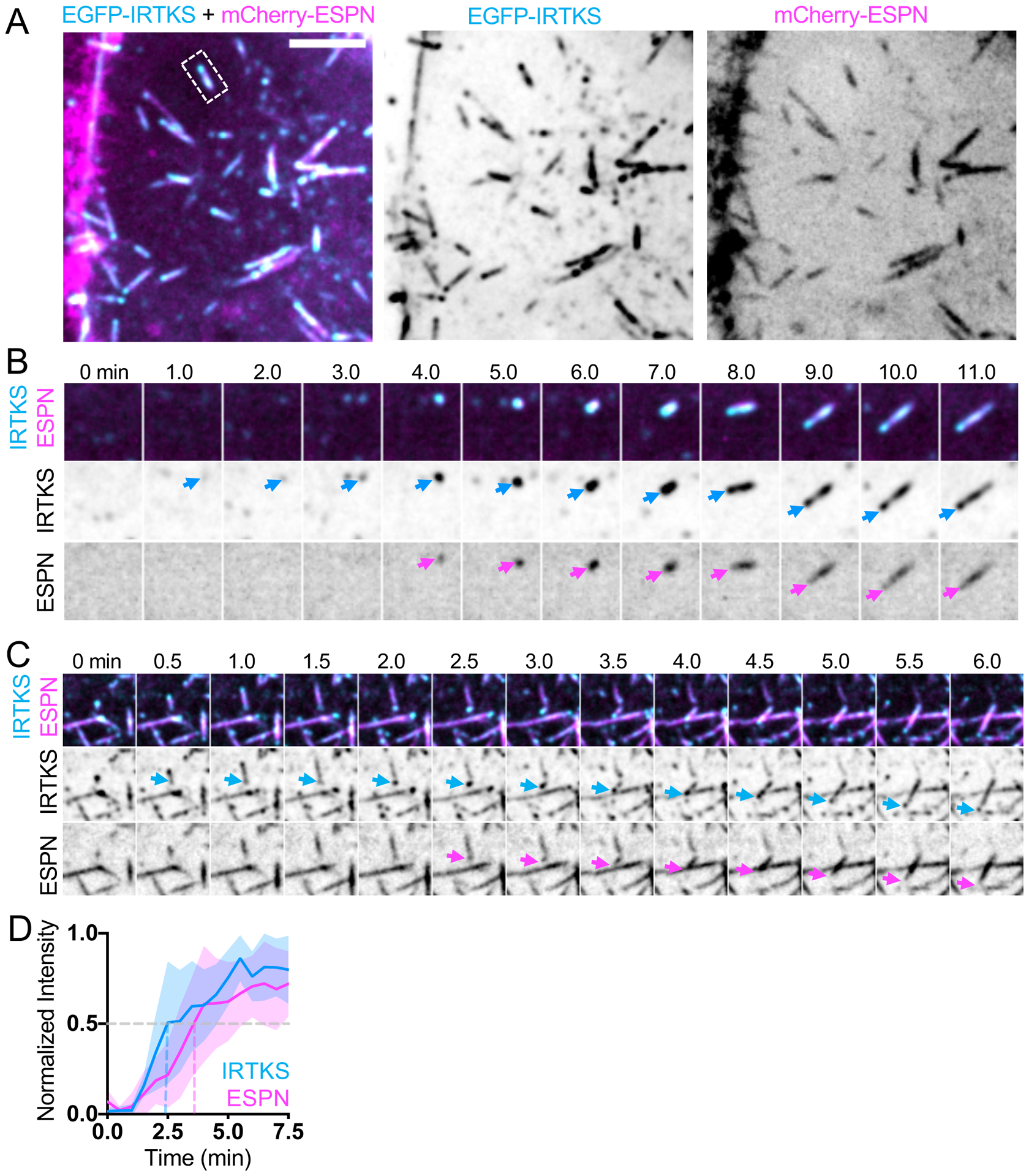
(A) Maximum intensity projection of a CL4 cell expressing mCherry-ESPN (magenta) and EGFP-IRTKS (cyan). Merge (left), EGFP-IRTKS (middle), mCherry-ESPN (right). Dashed box indicates microvillus shown in B. Scale bar = 5 μm. (B) Montage of a de novo microvillus growth event in a cell expressing EGFP-IRTKS and mCherry-ESPN. Arrows denote the presence of EGFP-IRTKS (cyan) or mCherry-ESPN (magenta). Box width = 4 μm. Related to Video S5 (C) Montage of daughter microvillus growing from pre-existing mother bundle in a cell expressing EGFP-IRTKS and mCherry-ESPN. Arrows denote EGFP-IRTKS (cyan) and mCherry-ESPN (magenta) of the daughter microvillus. Box width = 6 μm. (D) Normalized intensity vs. time curve of CL4 cells expressing EGFP-IRTKS and mCherry-ESPN; n = 9 events from 4 cells. T = 0 is defined as −3 frames (1.5 min) before the appearance of the EGFP-IRTKS signal. All images shown are maximum intensity projections. Dashed lines indicate point at which curves cross a normalized intensity of 0.5. For all curves, the solid line represents the mean and shading represents SD.
