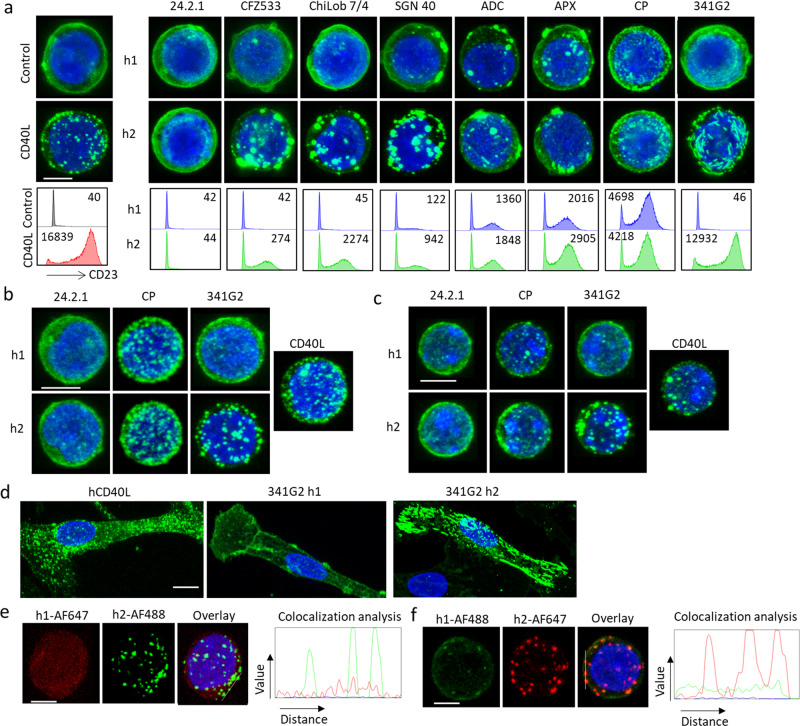
Fig. 1. CD40 agonists induce differential CD40 clustering.
a Upper panels: Jurkat-hCD40ECD-GFP cells were treated with 10 µg/mL anti-CD40 mAbs of either hIgG1 (h1) or hIgG2 (h2) isotype as indicated for 1 h, and then fixed with methanol, nucleus stained with DAPI and imaged using a Leica SP8 confocal microscope. Lower panels: B cells isolated from hCD40Tg/FcγR null mice were incubated with various anti-CD40 mAbs at 10 µg/mL as indicated for 3 days and then stained for surface expression of CD23 and analysed by flow cytometry, CD23 MFI indicated within histogram was quantified by Flowjo Software. b Normal human B cells isolated from healthy donor PBMC, or c B cells isolated from hCD40Tg mice were stained with AF488-labelled anti-CD40 mAbs as indicated for 1 h and then fixed with methanol, nucleus stained with DAPI and imaged using a Leica SP8 confocal microscope. d Human monocyte-derived DCs were stained with 10 µg/mL AF488-labelled hCD40L, 341G2 h1 or 341G2 h2 for 1 h and then fixed with methanol, nucleus stained with DAPI and imaged using a Leica SP8 confocal microscope. e Jurkat-hCD40ECD cells were co-stained with 341G2 h1-AF647 and 341G2 h2-AF488 or f co-stained with 341G2 h1-AF488 and 341G2 h2-AF647 for 1 h, and then fixed with methanol, nucleus stained with DAPI and imaged using a Leica SP8 confocal microscope; co-localisation analysis performed using ImageJ. All images are representative of at least ten images from at least two independent experiments. Scale bar, 4 µm.