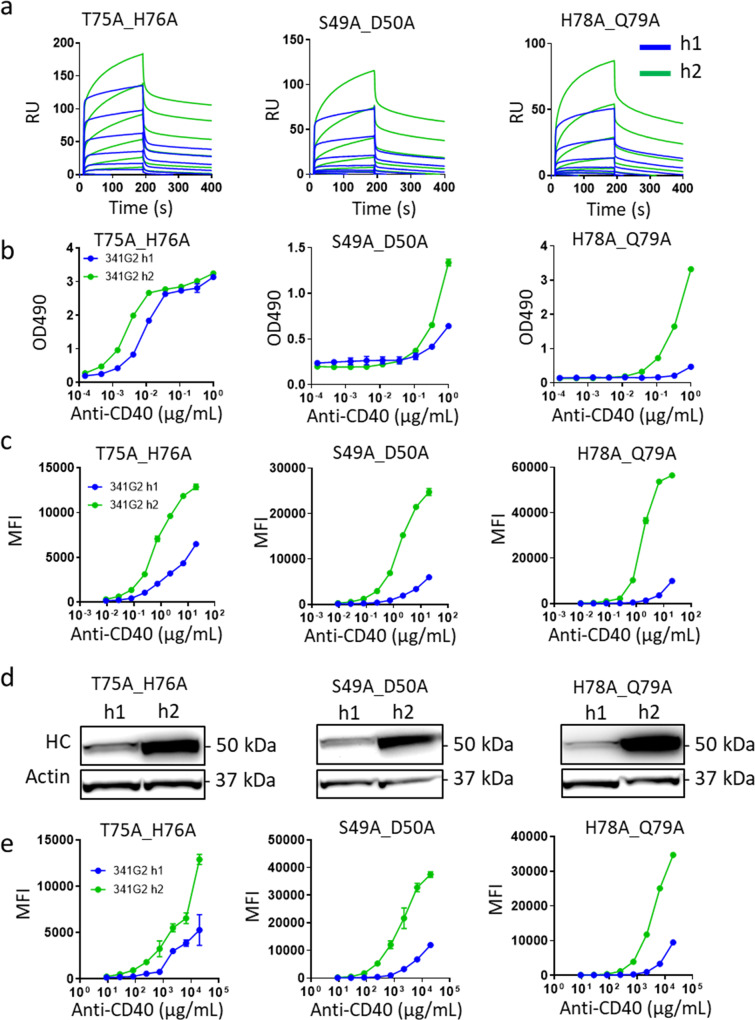
Fig. 6. hIgG2 confers higher binding avidity to low-affinity antigen and exhibits self-association.
a Recombinant soluble His-tagged CD40ECD mutants were captured by anti-His mAb pre-immobilised onto a CM5 chip, and then 341G2 h1 or h2 were injected at 1000, 333, 111, 37, 12.3, 4.1 or 0 nM using a Biacore T200 instrument. The association phase lasted for 180 s and the dissociation phase lasted for 300 seconds. b Recombinant soluble WT or mutant CD40ECD was coated onto ELISA plates at 5 µg/mL overnight; the next day, plates were washed and incubated with serially diluted 341G2 h1 or h2 for 1 h and then bound hIgG was detected by anti-hFc-HRP. Means ± SEM, n = 3. c CHO-k1 cells expressing various CD40 mutants on their surface as indicated were incubated with serially diluted 341G2 h1 or h2 for 30 min and then bound hIgG was detected by secondary anti-hFc-PE using flow cytometry. Means ± SEM, n = 3. d CHO-k1 cells expressing various CD40 mutants on their surface as indicated were incubated with 20 µg/mL 341G2 h1 or h2 for 30 min and then cells were lysed and the lysates subject to detection of hIgG by Western blotting as described in Methods. e CHO-k1 cells expressing various CD40 mutants on their surface as indicated were fixed with 4% PFA and then incubated with serially diluted 341G2 h1 or h2 for 30 min and bound hIgG was detected by secondary anti-hFc-PE using flow cytometry. Means ± SEM, n = 3. All data are representative of at least 3 independent experiments.