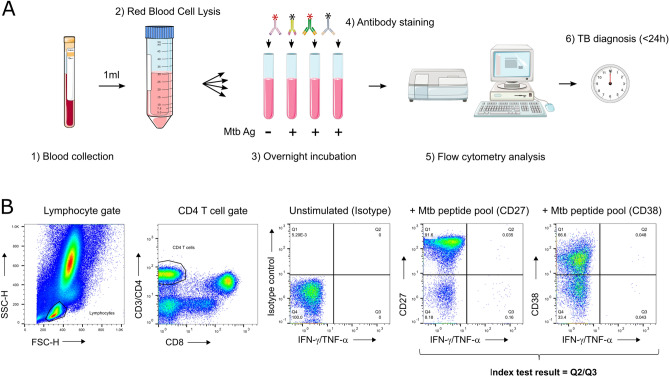
Figure 2.
(A) TAM-based assay procedure overview from blood collection to delivery of results within 24 h. Briefly, a single millilitre of fresh blood was subjected to red blood cell lysis (steps 1 & 2) and white blood cells evenly split between 4 tubes before overnight stimulation (step 3). The following morning, cells were fixed and stained with fluorescent antibodies as detailed in the methods section (step 4). Samples were immediately acquired on a FACSCalibur delivering final results within 24 h following phlebotomy (steps 5 & 6). This figure was created using objects from Servier Medical Art, free to share and adapt, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC BY 3.0) (http://smart.servier.com/). (B) Representative gating strategy of the TAM-based assay adapted for a 2-laser flow cytometer FACSCalibur apparatus. First, a gate based on Forward- (FSC) and Side-Scattered (SSC) signals is drawn to isolate lymphocytes from other blood cell types. Second, a CD4 T cell gate is obtained by tearing apart non-T cells in the y-axis from CD8 T cells in the x-axis. This gating strategy is applied to compare cytokine production and expression of CD27 or CD38 by CD4 T cells in samples stimulated or not with a Mycobacterium tuberculosis peptide pool. The index test result is obtained by dividing the frequency of CD4 T cells producing IFN-γ or TNF-α that express the investigated biomarker (Quadrant 2, Q2) by the frequency of those that did not express the biomarker (Q3).