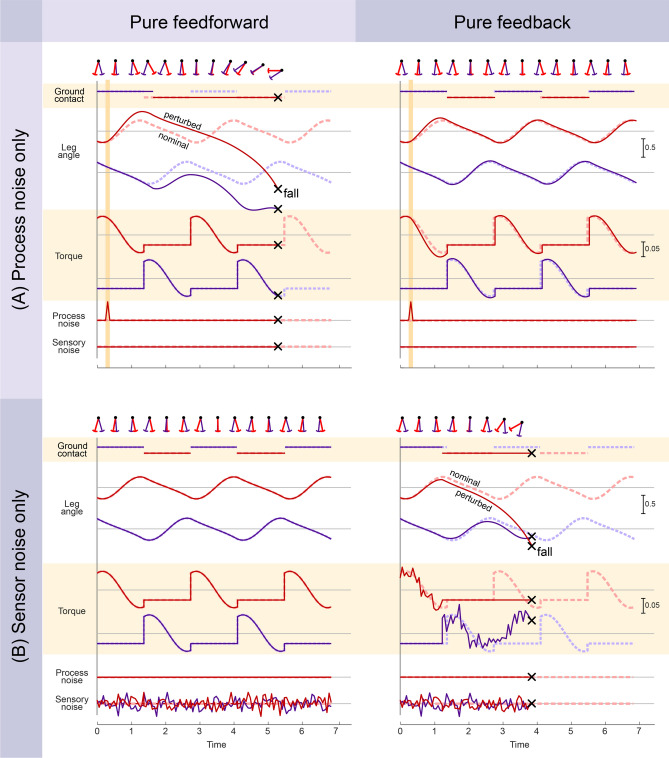
Figure 3.
Pure feedforward and pure feedback (left and right columns, respectively) are adversely affected by (A) process and (B) sensor noise. Process noise refers to disturbances from the environment or imperfect actuation, and sensor noise refers to imperfect sensing. Plots show ground contact condition, leg angles, commanded leg torques, and noise levels versus time, including both the nominal condition without noise (dashed lines), and the perturbed condition with noise (solid lines). With an impulsive, process noise disturbance, pure feedforward control tended to fall, whereas pure feedback was quite stable. With sensor noise alone, pure feedforward was unaffected, but pure feedback tended to fall.