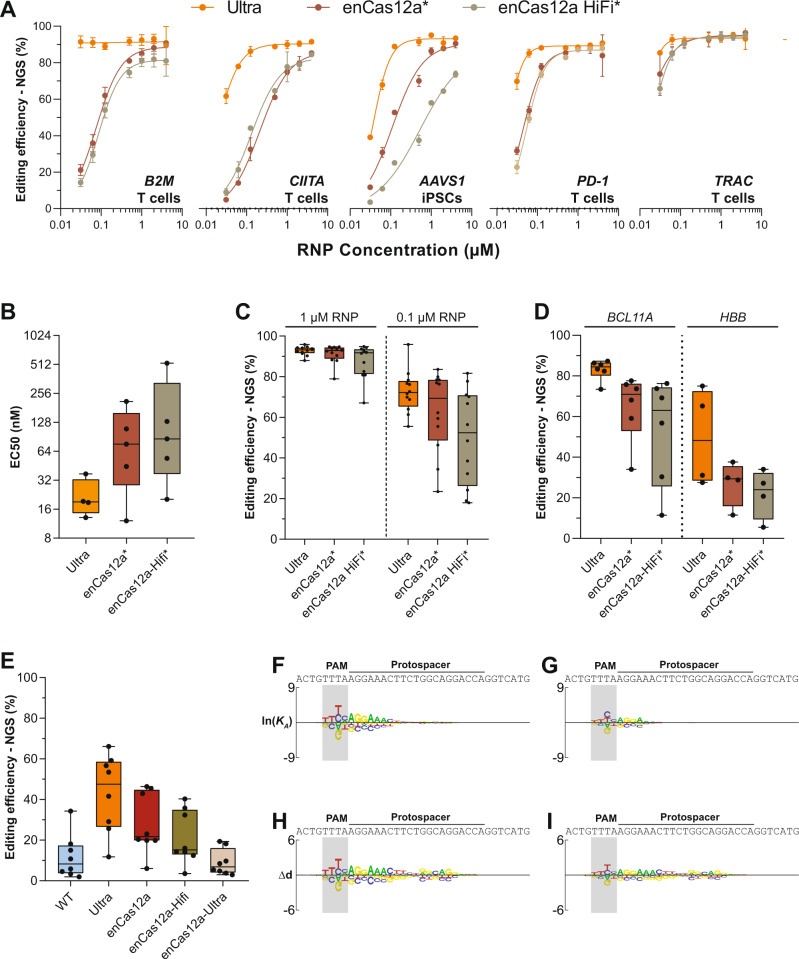
Fig. 4. AsCas12a Ultra is more specific and potent than enCas12a.
A The on-target editing efficiencies of Ultra, enCas12a, and enCas12a-Hifi across a wide range of RNP dosages at 5 target sites in primary cells (n = 5). Data are presented as mean values ± SD. *: enCas12a and Hifi with published NLS sequence. B The estimated EC50 of editing for each nuclease (n = 4). AsCas12a Ultra is ~4-fold more active than enCas12a (19 nM vs. 76 nM). C Editing efficiencies of AsCas12a Ultra, enCas12a and enCas12a-Hifi over 12 target sites of B2M locus in primary T cells (n = 12). Each data point represents a different guide at a unique location within the locus. D Editing efficiencies of AsCas12a Ultra, enCas12a and enCas12a-Hifi targeting BCL11A (n = 5) and HBB (n = 4) loci in HSPCs. Each data point represents a different guide at a unique location within the locus. E Editing efficiencies of WT, AsCas12a Ultra, enCas12a, enCas12a-Hifi and enCas12a-Ultra RNPs (50 nM) over 8 target sites in HEK293 cells (n = 8). Note: nucleases with identical NLS sequences were used in this experiment. F, G DNA binding specificities of enCas12a (F) and enCas12a-Ultra (G) as measured by Spec-seq/SEAM-seq. H, I DNA cleavage specificities of enCas12a (H), and enCas12a-Ultra (i) as measured by Spec-seq/SEAM-seq. While the general pattern of specificity remained the same, the intrinsic DNA sequence specificities of enCas12a and enCas12a-Ultra are systematically lower than AsCas12a Ultra (Fig. 1E, G) across the entire protospacer. Raw source data are provided in the Source Data File.