Fig. 8. Smad7 cooperates with AKT to induce cholangiocarcinoma development in mice.
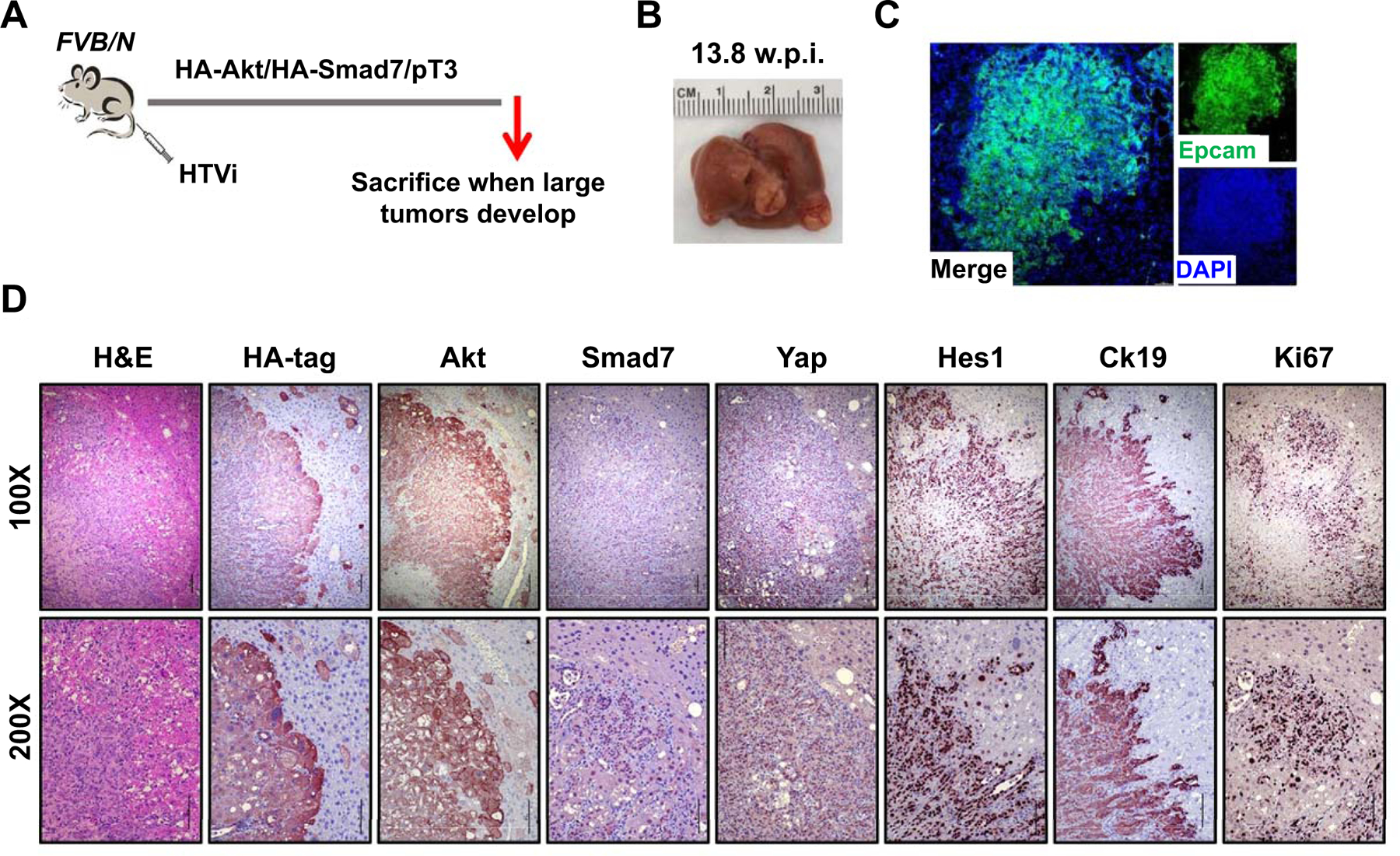
(A) Study design. FVB/N mice were injected with Akt/Smad7/SB (N=8) plasmids. Mice were monitored and sacrificed when moribund. (B) Macroscopic image of an Akt/Smad7 mouse showing the presence of large tumor nodules on the liver surface. (C, D) Immunofluorescence (C) and immunohistochemistry images (D) showing that Akt/Smad7 mice express the injected transgenes (HA-tag; Akt, and Smad7) as well as markers of Yap (Yap) and Notch (Hes1) signaling activation. Ck19 and Ki67 staining indicate the cholangiocellular differentiation and the proliferative features of Akt/Smad7 tumor lesions. Scale bars: 200 μm for 100X, 100μm for 200X. Abbreviation: HTVi, hydrodynamic tail vein injection.
