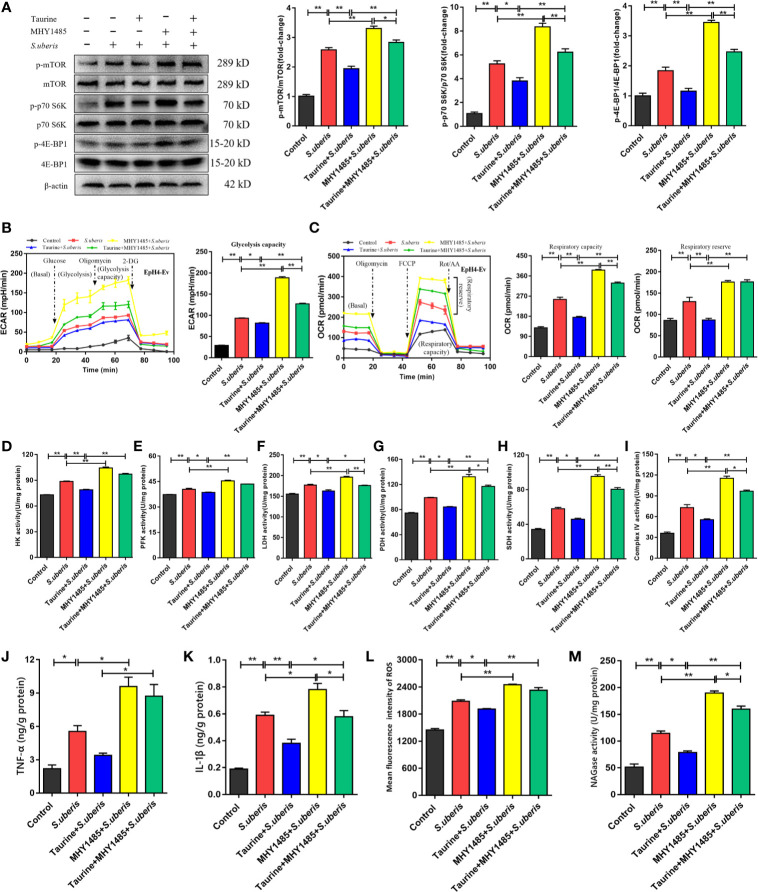
Figure 6.
Taurine regulates metabolic alterations in S. uberis infection by inhibiting the mTOR pathway. (A) EpH4-Ev cells were pretreated with taurine for 24 h and infected with S. uberis in mid-exponential phase (MOI = 10) for 3 h at 37°C. The cells were pretreated with 100 nM MHY1485 (mTOR activator) for 24 h prior to S. uberis infection. The protein-expression levels of mTOR, p70 S6K, and 4E-BP1, as well as the levels of each phosphorylated protein (p-mTOR, p-p70 S6K, and p-4EBP1) were determined by western blotting. (B, C) EpH4-Ev cells were pretreated with taurine for 24 h and then stimulated with inactivated S. uberis (MOI = 100) for 3 h at 37°C. The cells were pretreated with 100 nM MHY1485 for 24 h before S. uberis infection. Real-time changes in the ECAR (B) and OCR (C) levels in EpH4-Ev cells were determined. (D–I) The relative activities of enzymes driving glycolysis and OXPHOS were determined using commercial kits. (J, K) TNF-α and IL-1β levels in EpH4-Ev cell supernatants pretreated with 100 nM MHY1485 were measured by ELISA. (L) Intracellular ROS contents were evaluated by staining cells (10,000/sample) with DCFH-DA, followed by analysis using CellQuest Pro acquisition and FlowJo software. (M) Supernatant NAGase activities were determined using commercial kits. Data are represented as mean ± SEM (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.