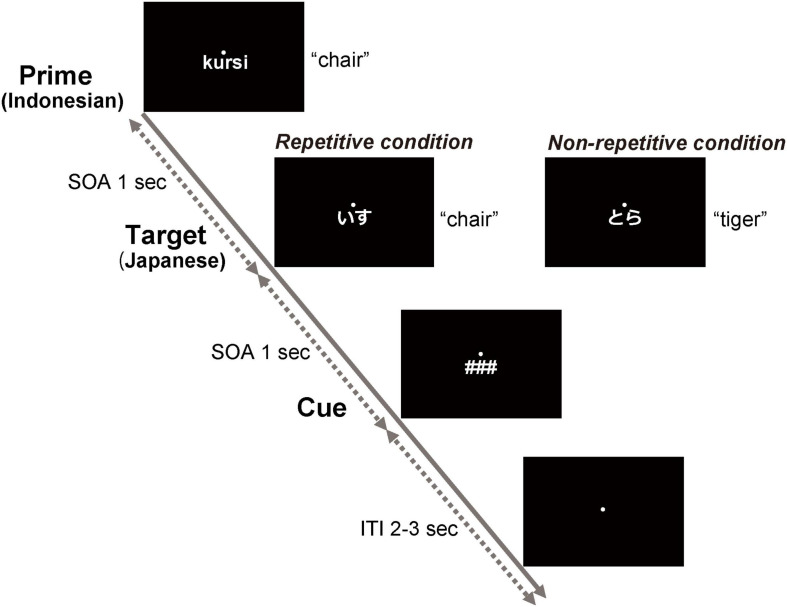
FIGURE 1.
Schematic representation of the repetition priming paradigm. The prime stimuli were Indonesian words written in alphabet, which the participants wrote in the learning activity. The target stimuli were Japanese words written in Japanese morphograms (kanji) and/or syllabograms (kana). The target words were Japanese translations of the prime stimuli in the repetitive condition (i.e., semantically repetitive). In the non-repetitive condition, the target words were not related to the prime stimuli. The prime, target, and cue were presented with a stimulus-onset asynchrony of 1 s. The intertrial interval between the offset of the cue and onset of the next prime was randomly set at 2–3 s. After the presentation of the cue (###), the participants answered whether the target word matched the prime word or not by clicking on a mouse with the right fingers.