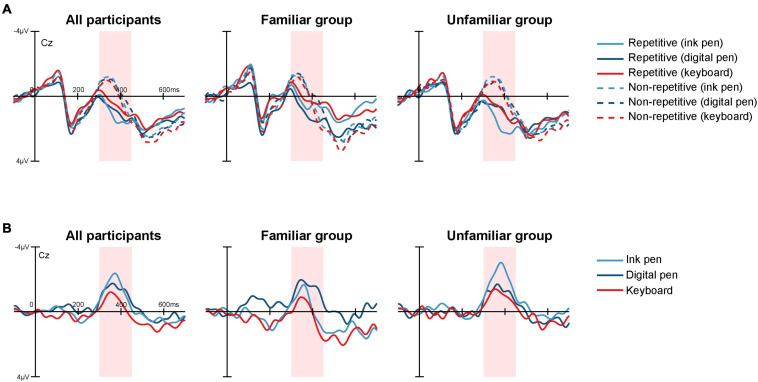
FIGURE 5.
ERPs at Cz (midline vertex) measured in the repetition priming paradigm. (A) The ERPs for the target words learned using an ink pen (light blue), a digital pen (dark blue), and a keyboard (red) in the repetitive (solid line) and non-repetitive (dashed line) conditions were averaged across all participants (left), for the members of the familiar group (middle), and those of the unfamiliar group (right). (B) The ERPs for the repetitive condition were subtracted from those for the non-repetitive condition for each writing tool. The differential ERPs had a negative peak at approximately 360 ms, which represents the repetition priming effect on N400. Mean amplitudes from 300 to 450 ms (shaded in pink) were used as electroencephalographic indices for learning effect. The amplitude was higher for words learned with the ink pen (light blue) or digital pen (dark blue) than for those learned using the keyboard (red).