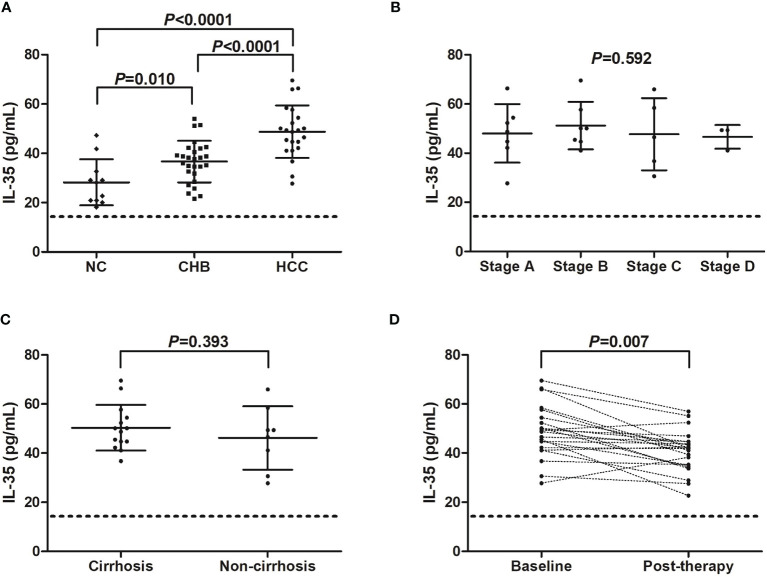
Figure 1.
IL-35 level in hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). (A) Serum IL-35 concentration was measured by ELISA in normal controls (NC, n=11), chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients (n=27), and hepatitis B-related HCC patients (n=22). Significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA and SNK-q test. (B) Serum IL-35 level was compared among hepatitis B-related HCC patients in BCLC stage A (n=7), stage B (n=7), stage C (n=5), and stage D (n=3). Significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA. (C) Serum IL-35 was also compared between hepatitis B-related HCC patients with cirrhosis (n=14) and without cirrhosis (n=8). Significance was assessed using Student t test. (D) Serum IL-35 was also measured in hepatitis B-related HCC patients who underwent hepatic carcinectomy (n=13) or TACE (n=9), and was compared between baseline and 2 months post therapy. The dotted line presented lower detection limit for IL-35 (15.6 pg/mL). Significance was assessed using paired t test.