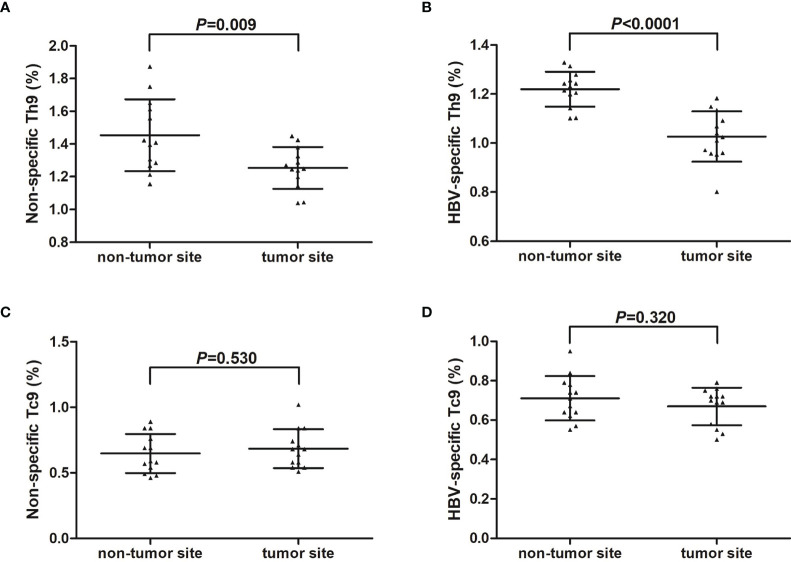
Figure 4.
Liver-infiltrating non-specific and HBV core-specific Th9/Tc9 cells in hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Intrahepatic lymphocytes (IHLs) were isolated from fresh HCC specimens and non-tumor site liver specimens in thirteen HCC patients (seven in stage A and six in stage B) who underwent hepatic carcinectomy. IHLs were stimulated with either phorbol myristate acetate (50 ng/ml)+ionomycin (1 μg/ml) (for non-specific stimulation) or HBsAg (for HBV-specific stimulation) in the presence of brefeldin A (10 μg/ml) for 6 hours, and were then stained with anti-CD3, anti-CD4, anti-CD8, and anti-IL-9. CD3+CD4+IL-9+ Th9 cells and CD3+CD8+IL-9+ Tc9 cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) The percentage of liver-infiltrating non-specific Th9 cells was compared between non-tumor site and tumor site. Significance was assessed using Student t test. (B) The percentage of liver-infiltrating HBV-specific Th9 cells was compared between non-tumor site and tumor site. Significance was assessed using Student t test. (C) The percentage of liver-infiltrating non-specific Tc9 cells was compared between non-tumor site and tumor site. Significance was assessed using Student t test. (D) The percentage of liver-infiltrating HBV-specific Tc9 cells was compared between non-tumor site and tumor site. Significance was assessed using Student t test.