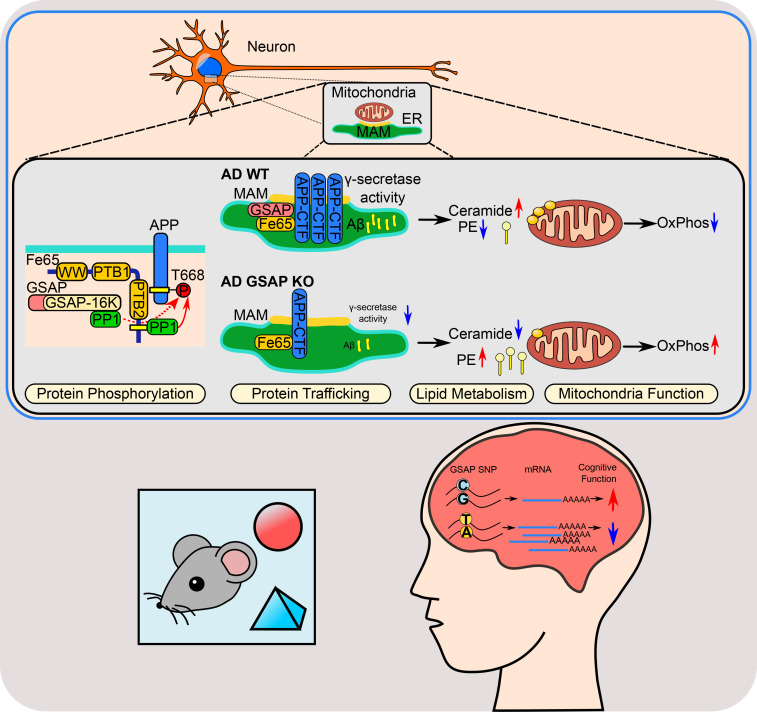
Figure 8.
Summary model. GSAP is involved in late-onset AD–related pathways, including protein phosphorylation, trafficking, lipid metabolism, and mitochondrial function. In neurons, GSAP forms a complex with Fe65–PP1–APP to regulate APP phosphorylation; depletion of GSAP decreases APP-CTF partitioning into lipid rafts (MAM) as well as γ-secretase activity for Aβ generation. These amyloidogenic products have detrimental effects on the cellular lipid homeostasis. Depletion of GSAP maintains a lipid environment with up-regulated PE and down-regulated Cer, which improves mitochondrial function. Functionally, we discovered that GSAP deletion restored novel recognitive function in an AD mouse model and provided evidence that a GSAP SNP is associated elevated GSAP expression correlated with AD. OxPhos, oxidative phosphorylation.