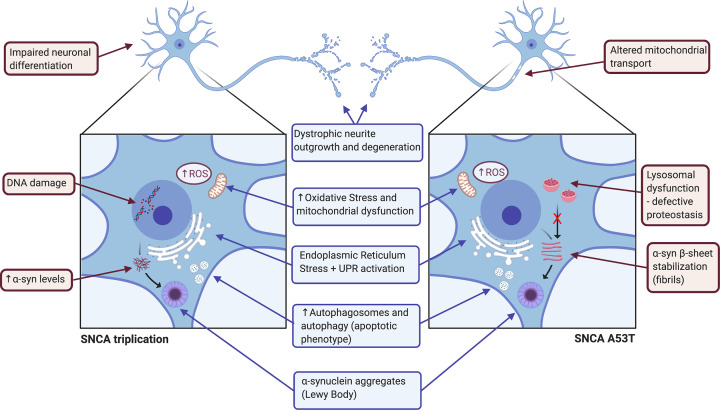
Figure 2. Summary of the cellular phenotypes reported in iPSC-derived neurons harboring SNCA triplication and A53T point mutation.
The common affected mechanisms for both mutations encompass impairment in neurite outgrowths, increased levels of oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction, increased ER stress, imbalanced apoptosis and accumulation of α-synuclein aggregates, are shown in blue. The individual effects of the triplication of SNCA are impaired neuronal differentiation, DNA damage and increased levels of α-synuclein, whereas the ones of A53T mutation of SNCA are mitochondrial transport dysfunction, lysosomal activity impairment and accumulation of α-synuclein in fibrils, shown in red.