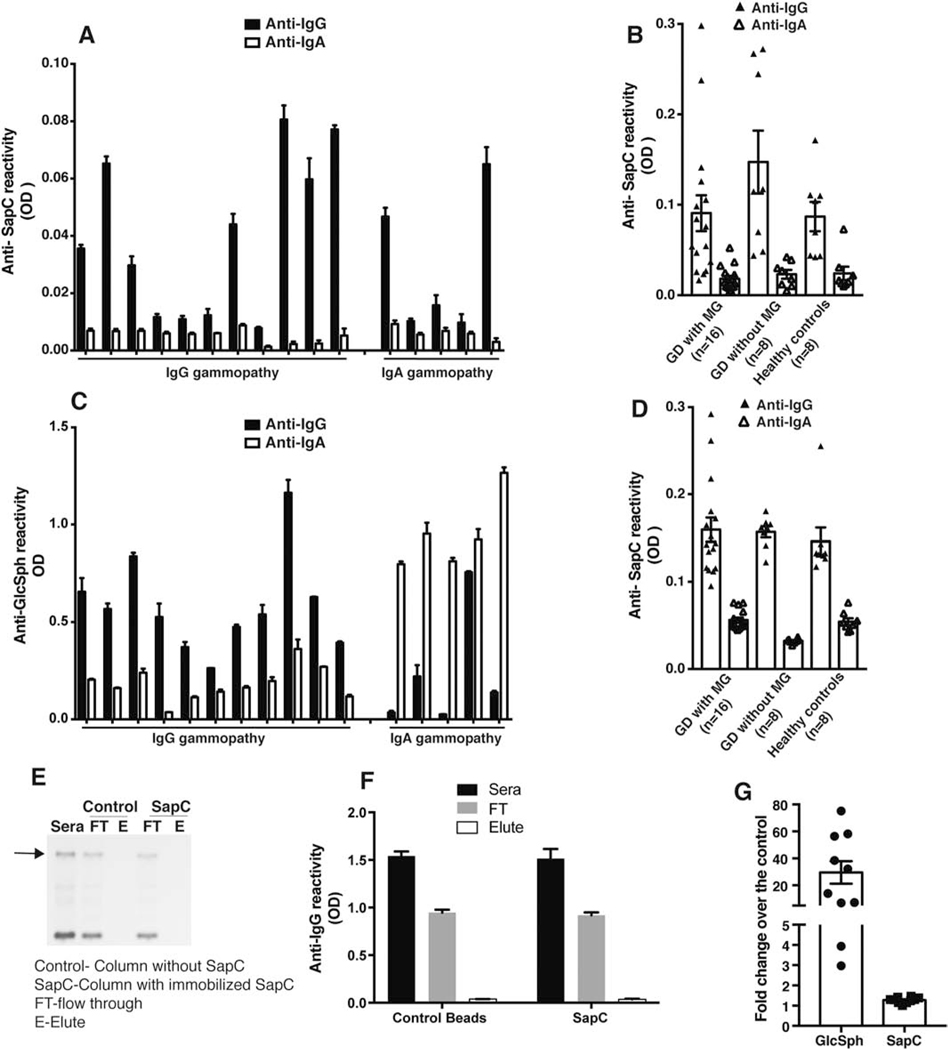
Figure 1. Immunoreactivity comparison between Glucosylsphingosine and Saposin C in the GD1 patient sera.
A) Capture ELISA was performed as described by Preuss et al 2018 [8] using anti-His mAb to capture recombinant purified human his tagged-saposin C (SapC) protein and Gaucher disease (GD) sera diluted 1:106. GD sera with monoclonal gammopathy (MG) with IgG (n=10) and IgA gammopathy (n=6) were used. B) Anti-SapC reactivity was compared in sera of GD sera with monoclonal gammopathy (MG) (n=16), GD sera without MG (n=8) and healthy donors (n=8). C) Glucosylsphingosine (GlcSph) reactivity for the same set of sera used for A) was analyzed by ELISA performed as earlier published paper[7] D) Direct ELISA was performed by coating purified human his tagged- SapC protein to wells of Nunc maxisorp plates followed by GD sera with monoclonal gammopathy (MG) with IgG (n=10) and IgA gammopathy (n=6) sera dilution of 1:106. E) Depletion of SapC specific clonal Igs from the sera of GD patient with MG. Representative blot shows serum protein electrophoresis (SPEP) analysis performed on sera from GD patient with MG after passing the sera through either control (without protein) or SapC immunoaffinity column prepared in accordance to Preuss et al[8]. FT-flow through; E-Elute. The experiment was repeated three times independently using at least 6 different sera from GD patients with MG. F) Flow through and elute fraction obtained from passing the sera through either the control or SapC immunoaffinity column was analyzed by clonal Ig class specific ELISA. G) Comparison of fold change of GlcSph and SapC levels in GD type 1 patient sera over the healthy controls (n=10).