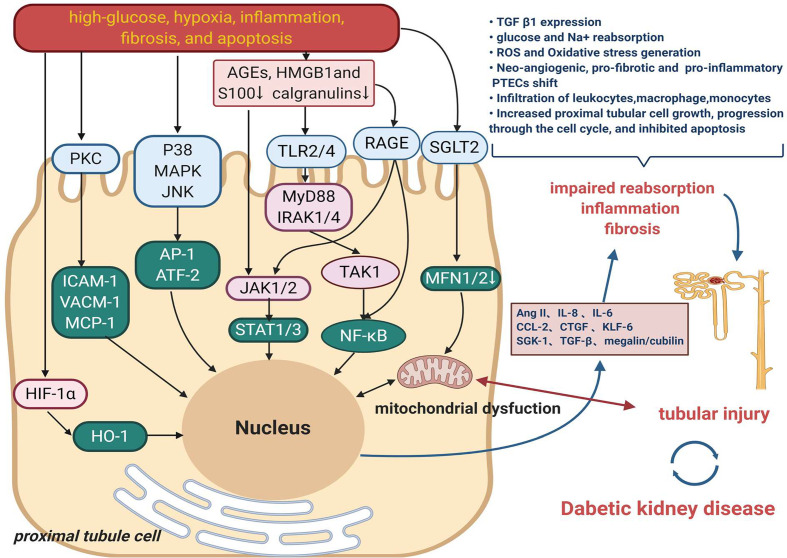
Figure 1.
The main mechanism of tubular damage in DKD. Diabetogenic stimuli including high-glucose, oxygen metabolic disorder, inflammation, fibrosis, and apoptosis result in a wide range of injured pathway such as MAPK, PKC signaling. High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), s100/calgranulins and advanced glycation end products (AGEs) are danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) that activate cell surface pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), induce signaling events to promote the development of inflammation in DKD. Another mechanism that also might contribute to tubular damage is the increased renal content of HIF1-α. Multiple effects on proximal tubule ultimately result in impaired reabsorption, inflammation and fibrosis, which contribute to tubule injury and therefore DKD.