Figure 1.
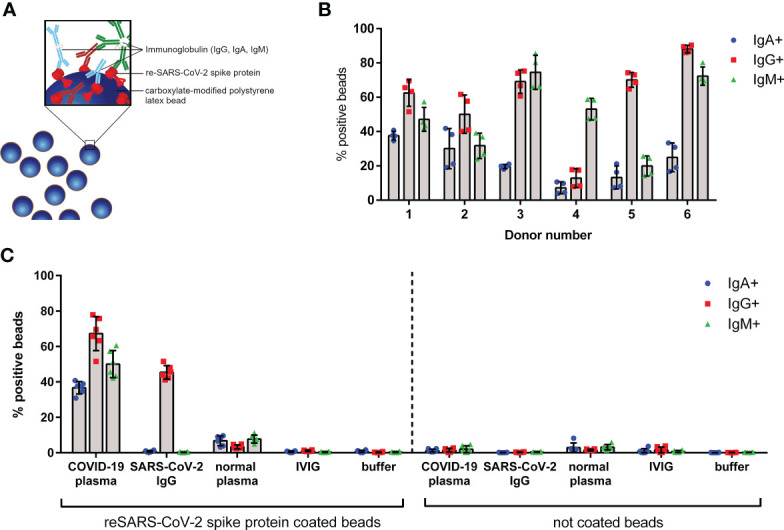
Characterization of SARS-CoV-2-like particles. (A) Schematic overview of fluorescent latex beads coated with recombinant (re-) SARS-CoV-2 spike protein; specific immunoglobulins of IgG (red), IgA (blue), and IgM (green) classes bound to the spike protein are shown. (B) IgG, IgA, and IgM bound on surface of SARS-CoV-2-like latex beads opsonized with different convalescent COVID-19 plasma donations (donor numbers 1–6). Coated beads were incubated with plasma from indicated donors for 45 min at 37°C. After washing, beads were stained with anti-IgG, anti-IgA, and anti-IgM detection antibodies and analyzed by flow cytometry. Percentage of positive beads for IgG, IgA, and IgM is shown; data represents mean of four independent experiments. (C) Control experiments show specific binding of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies to spike protein. Coated or non-coated beads were incubated with indicated plasma, immunoglobulins, or buffer for 45 min at 37°C and were stained as described in (B). Data represents mean of six independent experiments.
