FIG 2.
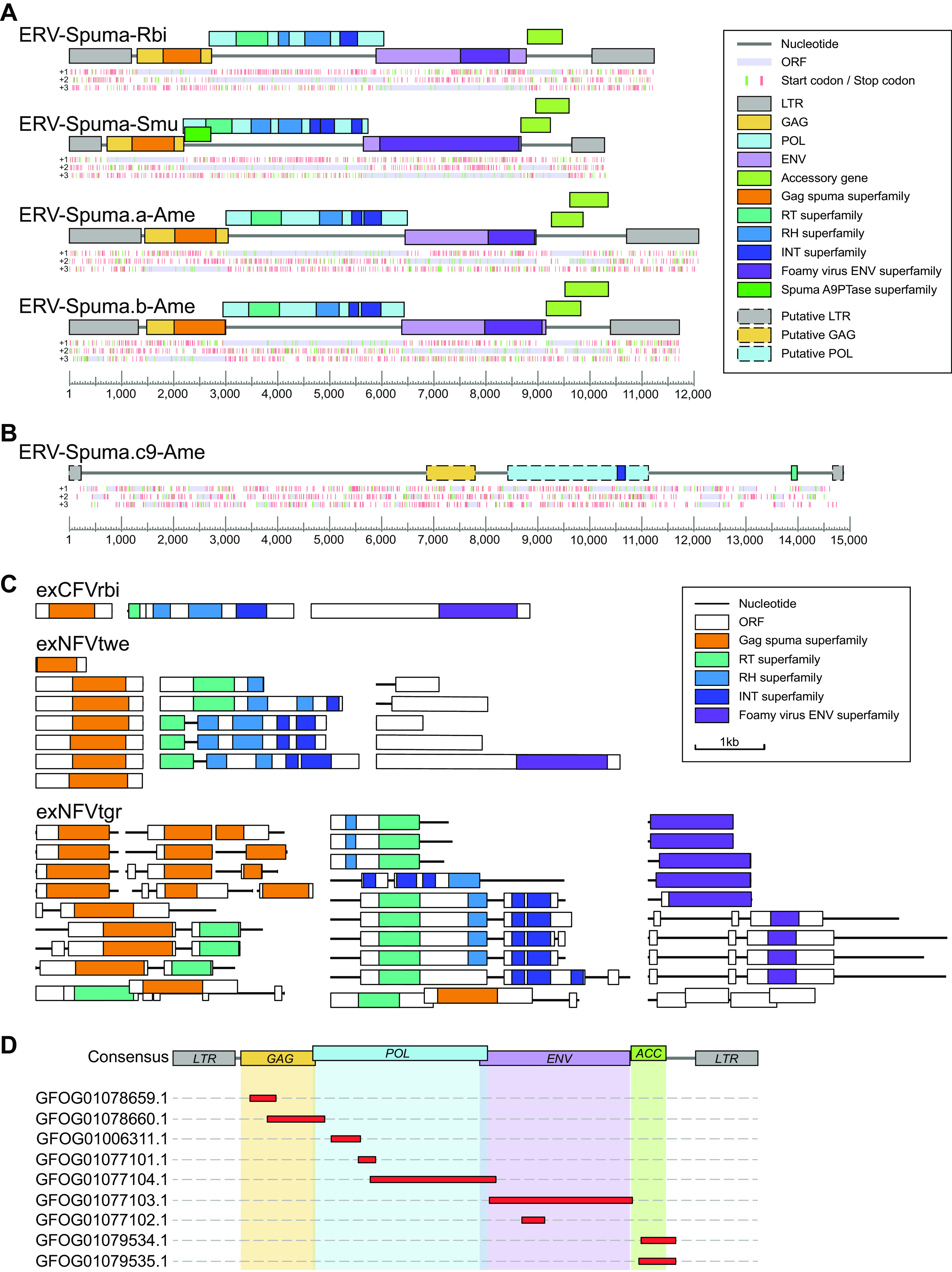
Genomic organization of novel EFVs and exFVs. (A) Consensus genomic organizations of four novel EFVs. The consensus genomes of EFVs are drawn to scale using lines and boxes. The distributions of stop (red) and start (green) codons in three forward frames (+1, +2, +3; from top to bottom) are shown under a genomic schematic diagram for each consensus genome. Putative open reading frames (ORFs) are shown in light purple and were used to determine viral coding regions. The predicted domain or regions that encode conserved proteins are represented by colored boxes. (B) Genomic organization of ERV-Spuma.c9-Ame. The only full-length ERV-Spuma.c9-Ame genome is drawn to scale using lines and boxes. The predicted putative domain or regions that encode conserved proteins are represented by colored dashed boxes. (C) Representative genomic structures of exFVs. The contigs and ORFs of exFVs are drawn to scale using lines and boxes. The predicted domain or regions that encode conserved proteins are represented by colored boxes. (D) Mapping result of the exCFVrbi genome against the consensus ERV-Spuma-Rbi genome. LTR, long terminal repeat; GAG, group-specific antigen gene; POL, polymerase gene; ENV, envelope gene; RT, reverse transcriptase; RH, RNase H.
