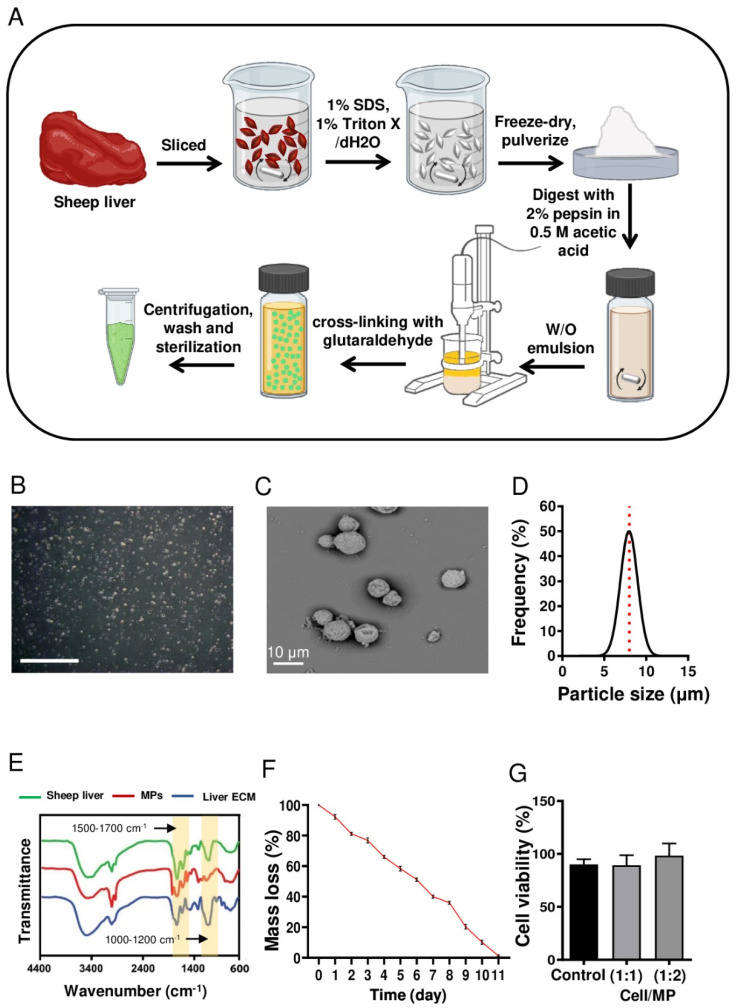
Figure 1.
Fabrication and characterization of liver-ECM-derived microparticles (MPs). (A) A schematic presentation of liver-ECM-derived MP fabrication. (B) Phase-contrast microscopy image of MPs (scale bar: 500 μm). (C) A representative scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image of the MPs. (D) Size distribution histogram of the MPs. (E) Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) spectra of intact and decellularized liver tissues and liver-ECM-derived MPs. (F) Mass loss of MPs in DPBS (pH 7.4, at 37 °C). (G) Cytocompatibility analysis of MPs by MTS assay on fibroblast cells cultured for 48 h on tissue culture polystyrene, with/without MPs, at different cell/MP ratios. (ECM: extracellular matrix; MPs: microparticles; SEM: scanning electron microscopy; FTIR: Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy; DPBS: Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline).