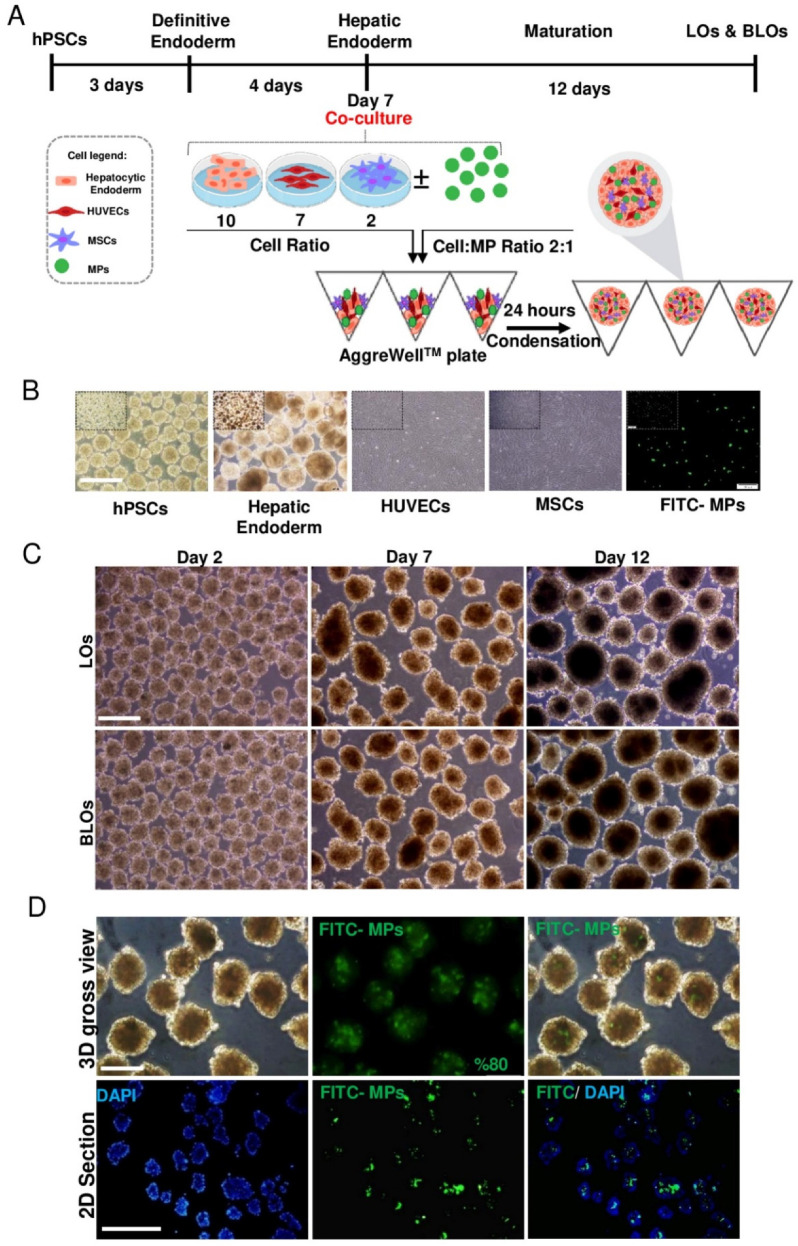
Figure 2.
Formation of LOs and BLOs from human pluripotent stem-cell-derived hepatic endoderm. (A) A schematic presentation of the stepwise protocol for differentiation of hESCs (RH5 cell line) towards HE and their coculture with HUVECs and MSCs (10:2:7 of HE:MSC:HUVEC), with/without MPs (2:1 cell:MP), in AggreWell™ plates. (B) Phase-contrast microscopy images of hPSCs, HE derived from hESCs, HUVECs, MSCs, and FITC-MPs (scale bar: 200 µm) (C) Phase-contrast microscopy images of cell aggregates on Days 2, 7, and 12 post-coculture (scale bar: 200 μm). (D) Visual illustration of MP incorporation within cell aggregates composed of three types of cells (HE, HUVECs, and MSCs; 10:7:2, respectively) using fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled MPs. Phase-contrast microscopy images (top left), fluorescence microscopy images (top middle), merged fluorescence microscopy image (top right), and paraffin-embedded cross-section (bottom) of the MP-incorporated cell aggregate. FITC-labeled MPs are visualized in green. The nuclei of cells were counterstained with DAPI. Scale bar: 200 (top) and 500 μm (below). HE: hepatic endoderm; HUVECs: human umbilical vein endothelial cells; MSCs: mesenchymal stem cells; LOs: liver organoids; BLOs: bioengineered liver organoids; hESCs: human embryonic stem cells; MPs: microparticles; FITC: fluorescein isothiocyanate.