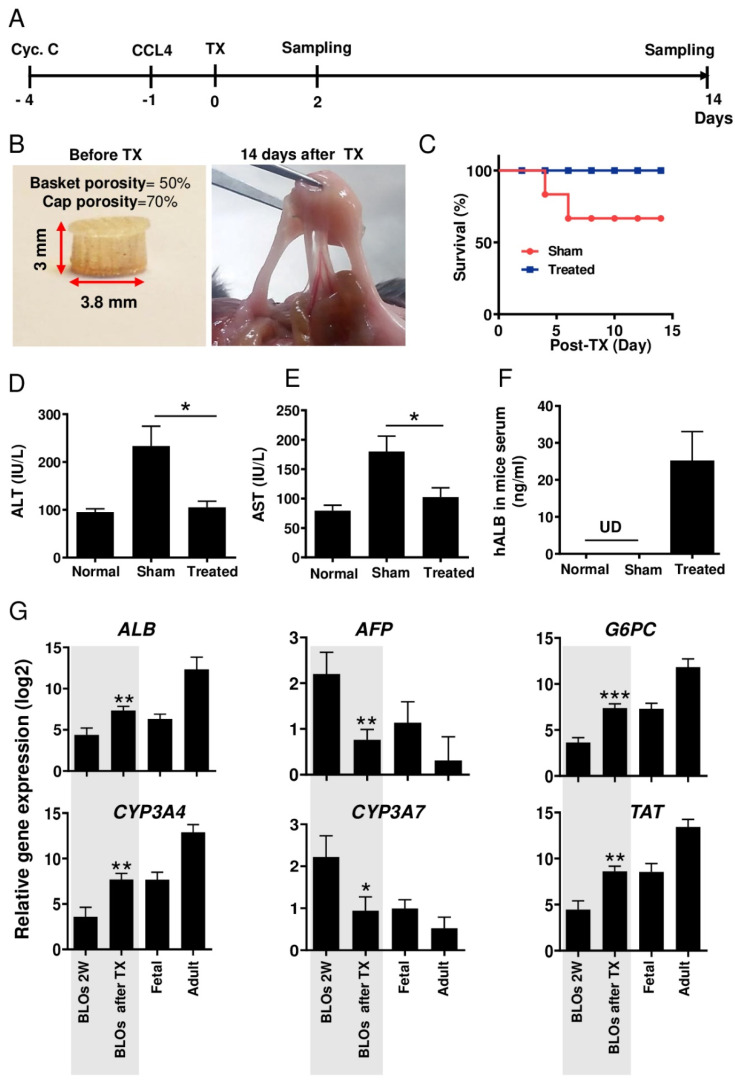
Figure 6.
Ectopic implantation of the BLOs in mice with acute liver injury. (A) The timeline representing the time points in the figure. (B) 3D-printed basket containing the BLOs, before (left) and after (right) transplantation. (C) A graphic presentation of the survival rate of the control and treated groups. (D,E) Biochemical assessment of blood sera from mice with acute liver injury treated with the BLOs. BLO transplantation led to significantly decreased alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) levels. (F) Human ALB was measured by ELISA in mice sera. Normal: normal mice; Control: CCl4-treated mice transplanted with empty baskets; Treated: CCl4-treated mice transplanted with 3D baskets containing approximately 1000 BLOs (n =8). Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed by using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-tests. * p < 0.05. (G) Relative gene expression of hepatic-specific genes (ALB, AFP, G6PC, CYP3A4, CYP3A7, and TAD) in the BLOs, before and after transplantation, and fetal and adult liver tissues as control groups. Data were normalized against GAPDH and are presented as fold changes compared with data obtained on coculture Day 0 as the calibrator. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 8). Statistical analysis was performed by using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-tests. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p< 0.001. BLOs: bioengineered liver organoids; 3D: three-dimensional; ALT: alanine transaminase; AST: aspartate transaminase; ALB: albumin; CCL4: carbon tetrachloride.