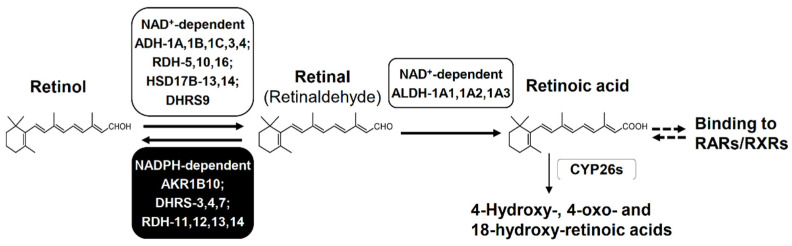
Figure 5.
Biosynthesis and degradation of retinoic acid. Retinol is oxidized to retinal by NAD+-dependent enzymes, but this step is reversible by NADPH-dependent reductases. Retinal is oxidized irreversibly to retinoic acid by NAD+-dependent enzymes. Retinoic acid activates RAR and RXR to initiate the transcription of target genes that regulate differentiation, apoptosis, and cell cycle arrest. Retinoic acid is also eliminated by conversion to its hydroxy- and/or oxo-metabolites. Abbreviations: ADH, alcohol dehydrogenase; RDH, retinol dehydrogenase; HSD17B, 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase; DHRS, dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR family) member; ALDH, aldehyde dehydrogenase; CYP26s, cytochrome P450 family 26 enzymes, RAR, retinoic acid receptor; and RXR, retinoid X receptor. DHRS9 is called RDHL, and ALDH-1A1, 1A2, and 1A3 are also called retinal dehydrogenase (RALDH)-1, 2, and 3, respectively.