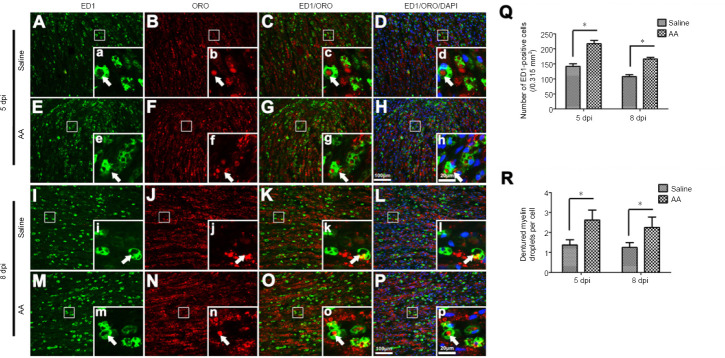
Figure 6.
Ascorbic acid (AA) enhances the infiltration and phagocytosis of macrophages in the injured nerve.
Immediately after sciatic nerve transection surgery, rats were intragastrically administered 400 mg/kg AA, which was followed by 200 mg/kg AA per day for 5 or 8 days. (A–P) ED1 immunofluorescence and ORO counterstaining show macrophages (white arrows) and denatured myelin (white arrows) in the injured nerves at 5 and 8 dpi. The numbers of ED1-positive cells and droplets of denatured myelin per macrophage in the AA group were significantly higher than in the saline group. (a-p) Higher magnification images of the boxes in A-P. Scale bars: 100 μm in A–P, 20 μm in a–p. (Q, R) The numbers of macrophages and droplets of denatured myelin per macrophage at 5 and 8 dpi. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 3 per group). *P < 0.05 (independent samples t-tests). dpi: Days post-injury; ED1: CD68; ORO: oil red O.