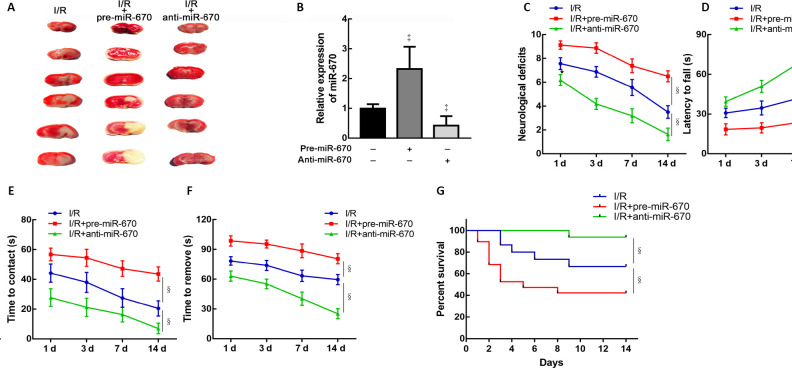
Figure 4.
MiR-670 exacerbates neurological deficits induced by ischemia and reperfusion injury.
(A) 2,3,5-Triphenyltetrazolium chloride stain of mouse brain tissue slices. (B) Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) assay of miR-670 in brain tissue after transfection (n = 9). Relative expression of miR-670 was calculated as the optical density ratio to that of the endogenous control (GAPDH). (C) Neurological deficits were evaluated by modified neurological severity scores in mice with altered miR-670 expression after cerebral I/R injury (n = 9). (D) Rotarod tests of mice with altered miR-670 expression (n = 9). (E, F) Adhesive removal tests of mice with altered miR-670 expression (n = 9). (G) Survival time of mice with altered miR-670 expression (n = 15–17). Data are presented as the mean ± SD. ‡P < 0.05, vs. I/R group; §P < 0.05 (Student’s t-test). The survival curves were generated by Kaplan–Meier analysis. anti-miR-670: An miR-670 antagomir; anti-NC: a non-sense sequence of the miR-670 antagomir; I/R: ischemia and reperfusion; pre-miR-670: an miR-670 agomir; pre-NC: a non-sense sequence of the miR-670 agomir; qPCR: quantitative polymerase chain reaction.