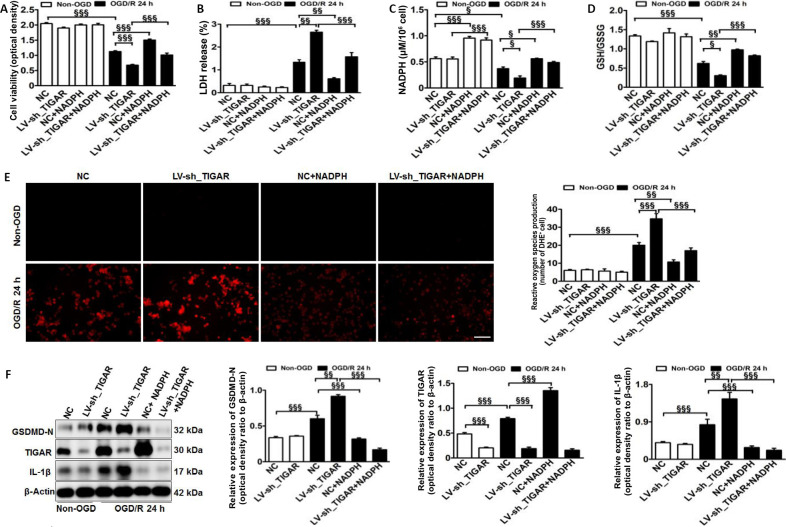
Figure 3.
TIGAR knockdown promotes microglial pyroptosis by increasing reactive oxygen species in vitro.
HAPI microglial cells were treated with LV-sh_TIGAR and subjected to OGD/R. Exogenous NADPH was added to HAPI microglial cells before OGD. (A) Cell viability was detected using a CCK-8 kit 24 hours after OGD/R. (B) Cell death was detected by LDH release 24 hours after OGD/R. Increased LDH release results in increased toxicity to cells and increased cell death. (C, D) The levels of NADPH (C) and rGSH (D) in HAPI microglial cells 24 hours after OGD/R. (E) Reactive oxygen species production was detected using DHE staining (red) 24 hours after OGD/R. Scale bar: 100 μm. (F) Quantification of TIGAR, GSDMD-N, and IL-1β in HAPI microglial cells 24 hours after OGD/R. Relative protein expression is shown as the ratio of the optical density of the target protein to that of β-actin. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 3/group). §P < 0.05, §§P < 0.01, §§§P < 0.001 (one-way analysis of variance followed by Bonferroni’s multiple-comparisons post hoc test). CCK-8: Cell Counting Kit-8; Con: Control; DHE: dihydroethidium; GSDMD-N: gasdermin D N-terminal; HIBD: hypoxic-ischemic brain damage; IL-1β: interleukin-1β; LDH: lactate dehydrogenase; LV-sh_TIGAR: vector containing short hairpin RNA of TIGAR; NADPH: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NC: LV-sh-scramble; OGD(/R): oxygen and glucose deprivation(/reoxygenation); TIGAR: TP53 induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator; HAPI: highly aggressively proliferating immortalized; rGSH: reduced glutathione.