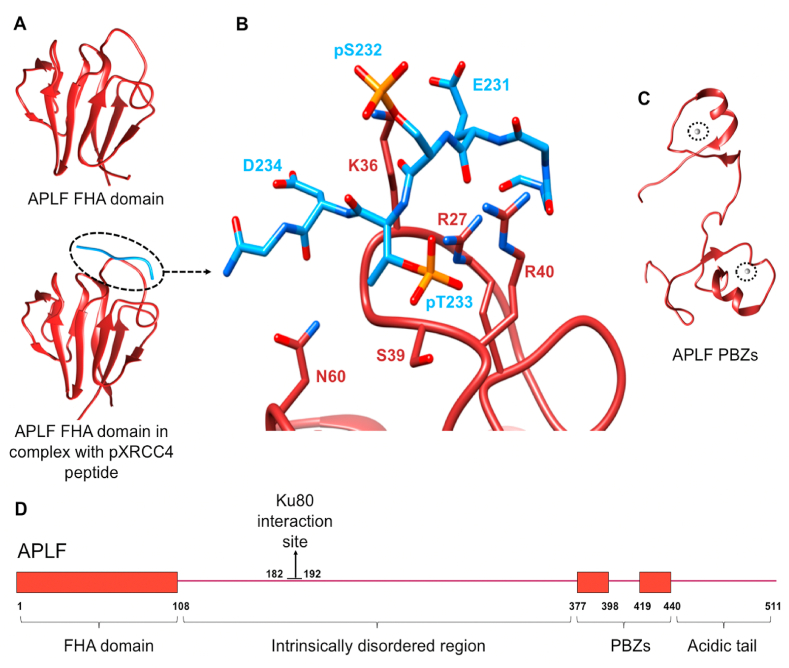
Fig. 7.
Structural information for APLF. A) Crystal structures of APLF FHA domain (1–105) (PDB code: 5W7W) (Kim et al., 2017), and FHA domain in complex with phosphorylated XRCC4 (pXRCC4) peptide (228–236) (PDB code: 5E50) (Cherry et al., 2015); B) The molecular interactions between APLF and pXRCC4 peptide. The core phosphothreonine (pT233) is involved in the hydrogen-bonding and ion-pair network of R27, S39 and R40 of APLF. R27 and N60 of APLF also form hydrogen bonds with the peptide backbone of pXRCC4. K36 of APLF is highly flexible but likely to have electrostatic interactions with E231, pS232 and D234 of pXRCC4; C) NMR structure of APLF PBZs, with the metal ions circled (PDB code: 2KUO), (Li et al., 2010); D) Schematic representation of the domains of APLF with the Ku80 interaction site labelled. APLF is coloured burgundy while the two zinc ions in APLF PBZs are coloured grey. XRCC4 is coloured blue.