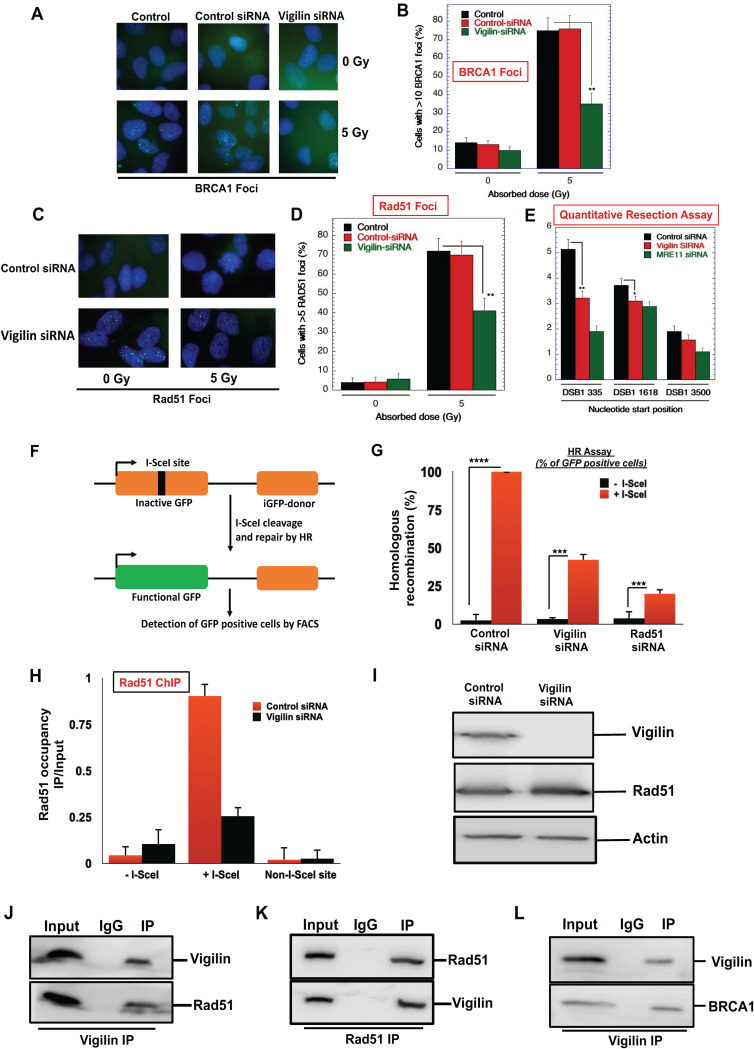
FIG 5.
Loss of vigilin impairs the homologous recombination repair pathway. (A to D) Quantification of cells for IR-induced BRCA1 and RAD51 focus formation in control and vigilin-depleted cells. (E) Quantitative resection assay showing the percentage of ssDNA formation in control and vigilin-depleted cells. The assay was done using the ER-AsiSI system, as described in Materials and Methods. Vigilin-depleted cells show significant reduction in ssDNA formation, Mre11-depleted ER-AsiSI U2OS cells were used as a positive control. Error bars are from three independently performed experiments. (F) Schematic diagram of the HR DR-GFP reporter assay cassette used to analyze homologous recombination. Homologous recombination was assessed using a direct repeat-green fluorescent protein (DR-GFP) cassette stably integrated at a single locus in H1299 cells. The DR-GFP gene is inactivated by insertion of an I-SecI site containing a stop codon. The downstream iGFP gene has 0.8-kb sequence homology to direct the repair of an I-SecI-cleaved inactive GFP, which results in the restoration of a functional GFP. (G) Cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs for 36 h, followed by transfection with I-SecI plasmid to induce DSB. Cells were assessed after 48 h by fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) analysis for GFP expression. Results indicate percentage of GFP-positive cells normalized to control cells from three independent experiments. (H) Vigilin depletion impairs recruitment of Rad51 to DSB sites. Cells were depleted with either control siRNA or vigilin siRNA, followed by induction of DSB by I-SceI. Rad51 occupancy was analyzed by chromatin immunoprecipitation at the I-SceI site in cells with and without the depletion of vigilin. The results represent standard errors from three independent experiments. (I) Rad51 protein levels in control and vigilin-depleted cells indicating that impairment of Rad51 recruitment to DSBs in cells lacking vigilin is not due to change in Rad51 protein levels. (J) Coimmunoprecipitation experiments showing vigilin interaction with Rad51. Vigilin was immunoprecipitated using vigilin-specific antibody; immunoprecipitated fractions were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-Rad51 antibodies. (K) Rad51 antibody was used for immunoprecipitation, and immunoprecipitated fractions were analyzed by Western blotting using antivigilin antibodies. (L) Immunoprecipitation experiment showing vigilin interaction with BRCA1. Vigilin was immunoprecipitated using a vigilin-specific antibody; immunoprecipitated fractions were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-BRCA1 antibodies.