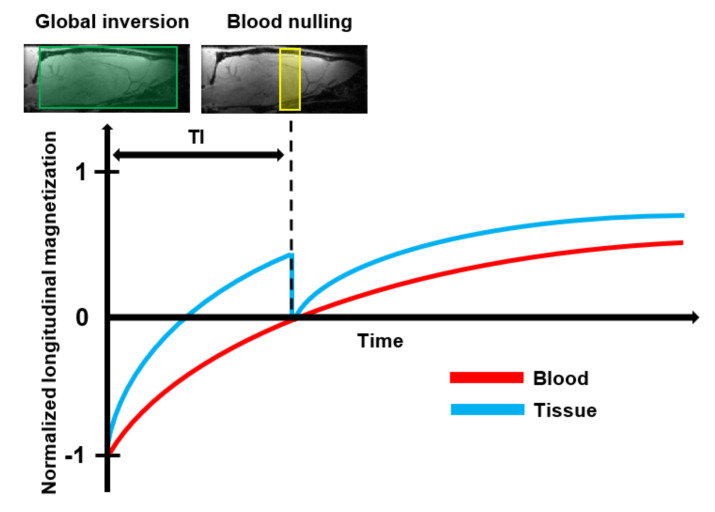
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of the basic principle of Vascular Space Occupancy (VASO) MRI: First, the spins of both blood and tissue are inverted by the use of a spatially non-slice-selective global 180° inversion pulse. After the global inversion pulse, the longitudinal magnetization of blood and tissue relax back at their spin-specific T1 relaxation rate. At the optimal Inversion Time (TI), when the longitudinal magnetization of the tissue crosses zero, an additional 90° excitation pulse is applied to null the blood signal. Then, an image is acquired that contains only signals that arise from the extravascular tissue.