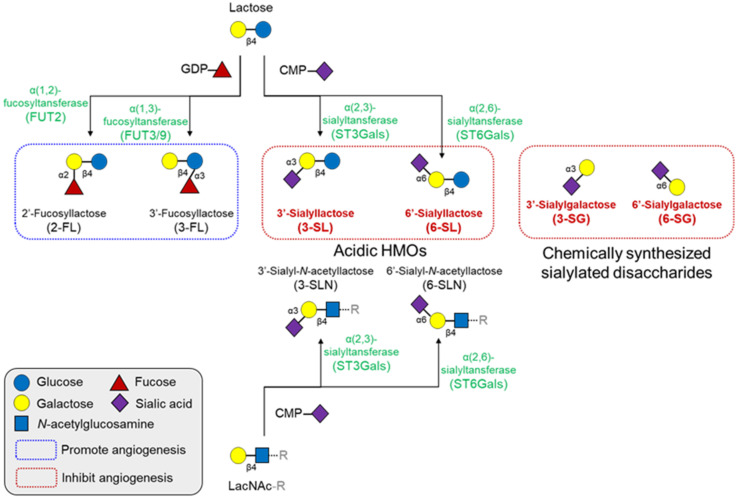
Figure 4.
Structures and synthetic pathways of major HMOs and their effects on angiogenesis. All HMOs consist of a lactose core or LacNAc core, with a few exceptions. These cores can be enzymatically elongated in repeats of LacNAc. The elongated HMO chains can be further decorated with fucosylation or sialylation by fucosyltransferases or sialyltransferases, respectively. Fucosylated HMOs generally promotes angiogenesis, but several sialyllactose analogs inhibit angiogenesis. CMP, cytidine monophosphate; GDP, guanosine diphosphate; HMO, human milk oligosaccharides; LacNAc, N-acetyllactosamine.