Fig. 1.
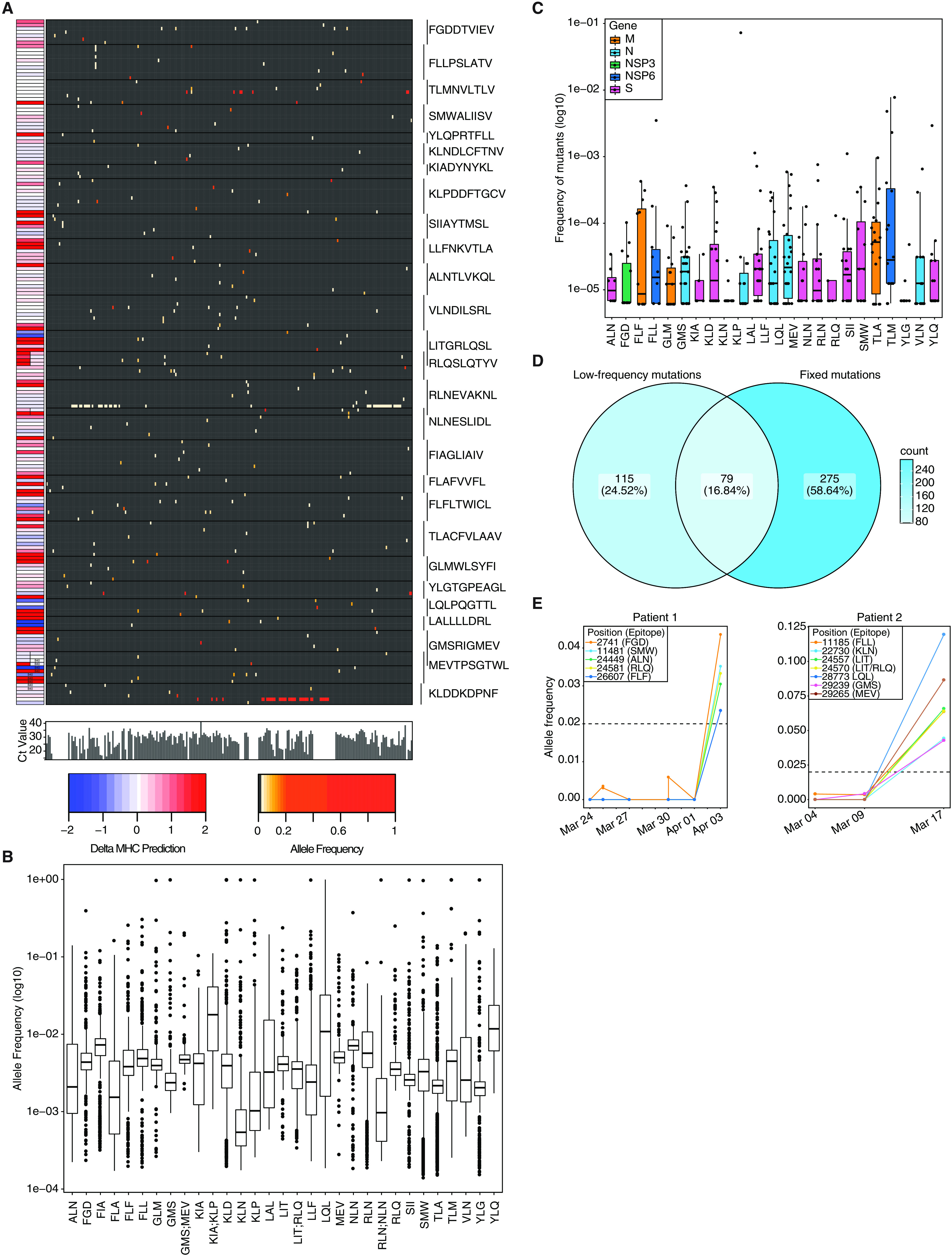
Nonsynonymous mutations are detected in SARS-CoV-2 CTL epitopes. A) Allele frequency of low-frequency mutations detected in 27 CTL epitopes. Epitopes are indicated on the right. The heatmap to the left indicates change in % ranks predicted by netMHCpan 4.1 (32). Bar plots below the large heatmap indicate viral loads as Ct values. B) Allele frequency of mutations in specified epitopes. Regions present in two epitopes are depicted separately. C) Frequency of global fixed mutations in CTL epitopes. D) Venn diagram depicting overlap between global fixed mutations and low-frequency variants. E) Mutations in CTL epitopes arise late in infection. Mutation frequency over time of two patients which were longitudinally sampled. Shown are variants that lead to nonsynonymous mutations in CTL epitopes. Patient 1 was sampled multiple times on the same day for some time points. Dashed lines indicate the detection limit for calling low-frequency mutations.
