Figure 1.
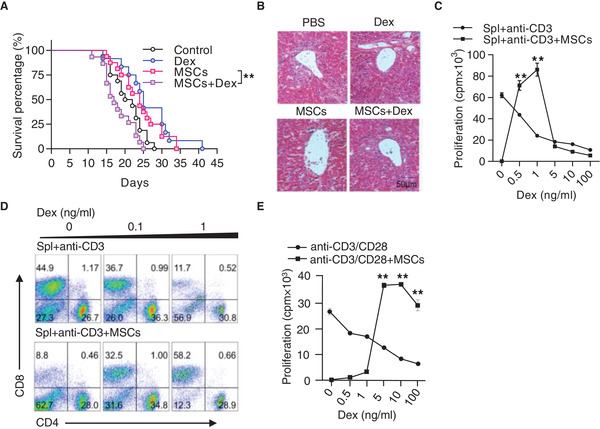
Steroids abolish the therapeutic effect of MSCs on aGvHD. A) Survival curves. Recipient mice (C57BL/6 × C3H F1) were lethally irradiated, followed by transplantation of bone marrow cells (5 × 106) and splenocytes (5 × 107) derived from C57BL/6 mice to induce aGvHD. Recipients were treated with MSCs (5 × 105) on days 5 and 7 after bone marrow transplantation and with and without Dex (2 mg kg−1) treatment (3 times per week). Data were pooled from 3 independent experiments (Control: n = 16, Dex: n = 12, MSCs: n = 16, Dex + MSCs: n = 15). B) Hematoxilin & eosin staining of the liver sections on day 21 after bone marrow transplantation. Scale bar: 50 µm. C) Dex reversed MSC‐induced immunosuppression on splenocyte proliferation. Splenocytes (2 × 105) were co‐cultured with MSCs (1 × 104) in the presence of anti‐CD3, with Dex treatment at indicated concentrations for 48 h. Cell proliferation was measured by 3H‐thymidine incorporation. Spl: splenocytes. D) Flow cytometric analysis of the percentages of CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells in the co‐culture system of activated splenocytes and MSCs, with or without Dex. E) Dex reversed MSC‐induced immunosuppression on CD8+ T cell proliferation. Splenic CD8+ T cells were isolated from C57BL/6 mice and co‐cultured with MSCs in the presence of anti‐CD3 and anti‐CD28, with or without Dex. Cell proliferation was assayed by the last 6‐h 3H‐thymidine incorporation. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. ** p < 0.01.
