Figure 4.
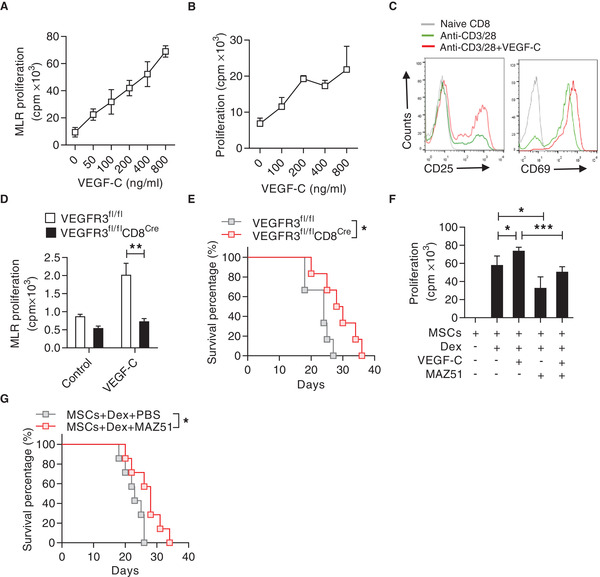
VEGF‐C promotes CD8+ T cell proliferation and exacerbates aGvHD. A) Promotion of mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) by VEGF‐C. Purified C57BL/6 CD8+ T cells (H2b) were co‐cultured with irradiated BALB/c (H2d) splenocytes and treated with VEGF‐C at indicated concentrations for 72 h. Cell proliferation was assayed by 3H‐thymidine incorporation. B) Proliferation of CD8+ T cells promoted by VEGF‐C. CD8+ T cells were stimulated by anti‐CD3 and anti‐CD28 in the presence of VEGF‐C at indicated concentrations for 48 h. Cell proliferation was measured by 3H‐thymidine incorporation. C) Flow cytometric analysis of the expressions of CD25 and CD69 on CD8+ T cells stimulated by anti‐CD3 and anti‐CD28, in presence or absence of VEGF‐C. D) VEGFR3 mediated the promotion effect of VEGF‐C on CD8+ T cell proliferation. CD8+ T cells were isolated from VEGFR3fl/fl or VEGFR3fl/flCD8Cre mice (C57BL/6) and co‐cultured with irradiated splenocytes from BALB/c mice for 72 h, with or without addition of VEGF‐C (800 ng mL−1). Cell proliferation was assayed by 3H‐thymidine incorporation. E) Survival curves of aGvHD mice induced by splenocytes from VEGFR3fl/fl and VEGFR3fl/flCD8Cre mice (n = 6 for each group). F) Blockade of VEGFR3 signaling by MAZ51 abolished the immune promotion induced by Dex and MSCs. CD8+ T cells were isolated and co‐cultured with MSCs plus anti‐CD3 and anti‐CD28, with or without Dex (10 ng mL−1), VEGF‐C (800 ng mL−1), or MAZ51 (10 µm). Cell proliferation was assessed by 3H‐thymidine incorporation. G) Survival rate of aGvHD mice with co‐administration of MSCs and Dex, or the combination of MSCs, Dex, and MAZ51. On day 5, recipients were injected with MSCs (5 × 106) and Dex (2 mg kg−1), or MAZ51 at 15 mg per kg per day (n = 7). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05, **p<0.01, and *** p < 0.001.
