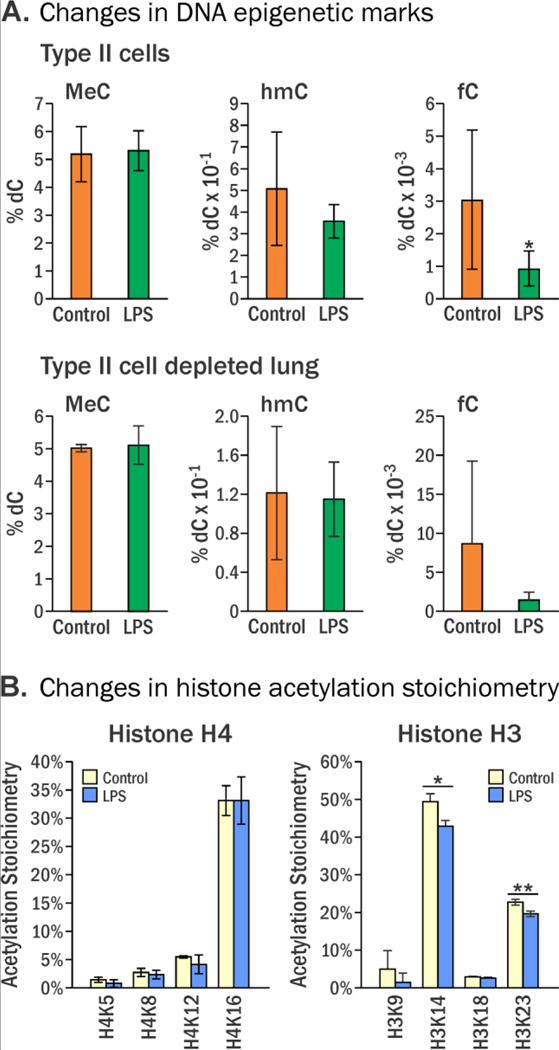
Figure 1.
Global levels of epigenetic DNA marks in type II alveolar lung cells of female A/J mice treated intranasally with LPS (4 μg/ day) for 4 days. Data represent mean values ± SD of at least three animals. A, MeC (n = 9), hmC (n = 9), and fC (n = 7), in genomic DNA isolated from type II cells. Statistics were calculated using the Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test, p-values: MeC (0.836), hmC (0.366), and fC (0.035). B, LPS-induced changes in histone lysine acetylation stoichiometry presented as percent acetylated. Statistical significance was evaluated between treated and control samples using a two-sided Student’s t-test (* p< 0.05, ** p<0.01). Histone acetylation stoichiometries were assessed to determine global gene activation by deacetylation due to exposure. Measured acetylation sites include lysines 5, 8, 12, and 16 on histone H4 and lysines 9, 14, 18, and 23 on Histone H3.