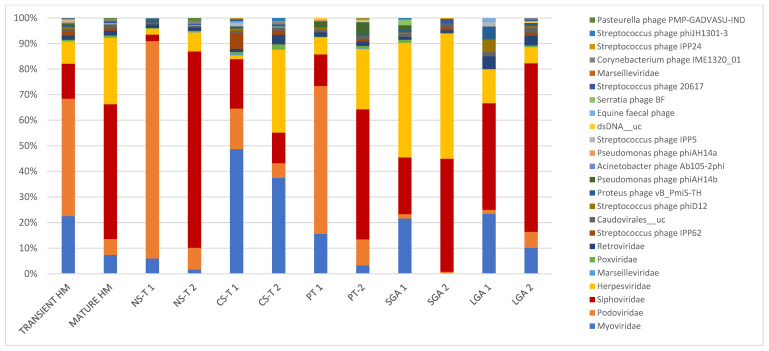
Figure 1.
In transient and mature human milk samples, the most abundant taxa in terms of mode of delivery form, prematurity, and birth weight for gestational age. Bacteriophages were predominant in transient human milk samples: in the vaginal delivery group at 98.4%, at 92.1% in the premature group, at 89.9% in the C-section group, and at 68.3% in the LGA group, except in the SGA group (only ~45% bacteriophages in TMS). Bacteriophages were also predominant in mature human milk samples; however, they were lower in mature human milk samples than in transient human milk samples (71.7% in the vaginal delivery group, 60.8% in the C-section-term group, 56% in the premature group, and 80.6% in the LGA group). Bacteriophages accounted for 45% of mature human milk samples in the SGA group. NS-T: normal spontaneous vaginal delivery-term; CS-T: cesarean delivery-term; PT: premature; SGA: small for gestational age; LGA: large for gestational age for all groups; 1: transient milk; 2: mature milk.